Spring Security Oauth2 Part 5
Oauth2 Login
Oauth2LoginConfigurer
Oauth2 인증 방식도 FormLogin, Basic Login 방식과 같이 Filter 기반으로 동작하게 되는데, 이때 각종 설정을 처리하는 Configurer 클래스가 존재한다.
init
init 메소드를 살펴보면 크게 4가지 객체를 초기화하는 과정이 존재한다.
- OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter: access token, Oauth2 Client 생성 등 Oauth2 기반의 인증을 위한 처리를 수행한다.
public void init(B http) throws Exception {
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter authenticationFilter = new OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter(
OAuth2ClientConfigurerUtils.getClientRegistrationRepository(this.getBuilder()),
OAuth2ClientConfigurerUtils.getAuthorizedClientRepository(this.getBuilder()), this.loginProcessingUrl);
authenticationFilter.setSecurityContextHolderStrategy(getSecurityContextHolderStrategy());
this.setAuthenticationFilter(authenticationFilter);
super.loginProcessingUrl(this.loginProcessingUrl);
if (this.loginPage != null) {
// Set custom login page
super.loginPage(this.loginPage);
super.init(http);
}
else {
Map<String, String> loginUrlToClientName = this.getLoginLinks();
if (loginUrlToClientName.size() == 1) {
// Setup auto-redirect to provider login page
// when only 1 client is configured
this.updateAuthenticationDefaults();
this.updateAccessDefaults(http);
String providerLoginPage = loginUrlToClientName.keySet().iterator().next();
this.registerAuthenticationEntryPoint(http, this.getLoginEntryPoint(http, providerLoginPage));
}
else {
super.init(http);
}
}
- Oauth2LoginAuthenticationProvider: Access Token을 요청하여 사용자 인증을 처리하는 provider
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationProvider oauth2LoginAuthenticationProvider = new OAuth2LoginAuthenticationProvider(
accessTokenResponseClient, oauth2UserService);
GrantedAuthoritiesMapper userAuthoritiesMapper = this.getGrantedAuthoritiesMapper();
if (userAuthoritiesMapper != null) {
oauth2LoginAuthenticationProvider.setAuthoritiesMapper(userAuthoritiesMapper);
}
http.authenticationProvider(this.postProcess(oauth2LoginAuthenticationProvider));
- OidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider: OIDC 기반으로 ID-Token을 통해 사용자 인증을 처리한다.
if (oidcAuthenticationProviderEnabled) {
OAuth2UserService<OidcUserRequest, OidcUser> oidcUserService = getOidcUserService();
OidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider oidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider = new OidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider(
accessTokenResponseClient, oidcUserService);
JwtDecoderFactory<ClientRegistration> jwtDecoderFactory = this.getJwtDecoderFactoryBean();
if (jwtDecoderFactory != null) {
oidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider.setJwtDecoderFactory(jwtDecoderFactory);
}
if (userAuthoritiesMapper != null) {
oidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider.setAuthoritiesMapper(userAuthoritiesMapper);
}
http.authenticationProvider(this.postProcess(oidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider));
}
else {
http.authenticationProvider(new OidcAuthenticationRequestChecker());
}
- DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter: 로그인 페이지를 생성하는 필터
this.initDefaultLoginFilter(http);
private void initDefaultLoginFilter(B http) {
DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter loginPageGeneratingFilter = http
.getSharedObject(DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter.class);
if (loginPageGeneratingFilter == null || this.isCustomLoginPage()) {
return;
}
loginPageGeneratingFilter.setOauth2LoginEnabled(true);
loginPageGeneratingFilter.setOauth2AuthenticationUrlToClientName(this.getLoginLinks());
loginPageGeneratingFilter.setLoginPageUrl(this.getLoginPage());
loginPageGeneratingFilter.setFailureUrl(this.getFailureUrl());
}
configure
configure 메소드에서는 Oauth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter을 생성하는 작업을 진행한다. 해당 filter은 AuthorizationCode를 요청하는 필터로, Oauth2LoginAuthenticationFilter 전에 동작한다.
OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter authorizationRequestFilter;
if (this.authorizationEndpointConfig.authorizationRequestResolver != null) {
authorizationRequestFilter = new OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter(
this.authorizationEndpointConfig.authorizationRequestResolver);
}
else {
String authorizationRequestBaseUri = this.authorizationEndpointConfig.authorizationRequestBaseUri;
if (authorizationRequestBaseUri == null) {
authorizationRequestBaseUri = OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter.DEFAULT_AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_BASE_URI;
}
authorizationRequestFilter = new OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter(
OAuth2ClientConfigurerUtils.getClientRegistrationRepository(this.getBuilder()),
authorizationRequestBaseUri);
}
그리고 아래의 4가지 Config 객체들이 등록되게 된다.
| Config | Description |
|---|---|
| AuthorizationEndpointConfig | 요청 코드 요청 관련 설정 |
| TokenEndpointConfig | access token 요청 관련 설정 |
| RedirectionEndpointConfig | 클라이언트에 대한 리다이렉트 설정 |
| UserInfoEndpointConfig | 유저 정보 요청 관련 설정 |
private final AuthorizationEndpointConfig authorizationEndpointConfig = new AuthorizationEndpointConfig();
private final TokenEndpointConfig tokenEndpointConfig = new TokenEndpointConfig();
private final RedirectionEndpointConfig redirectionEndpointConfig = new RedirectionEndpointConfig();
private final UserInfoEndpointConfig userInfoEndpointConfig = new UserInfoEndpointConfig();
Authorization Code 요청
Authorization Code를 요청하는 과정은 Oauth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter에서 동작한다.
주요 클래스
DefaultOauth2AuthorizationRequestResolver
Authorization Server로 Authorization Code를 요청할 때 활용되는 Oauth2AuthorzationRequest 객체를 생성하는 작업을 진행한다.
@Override
public OAuth2AuthorizationRequest resolve(HttpServletRequest request) {
String registrationId = resolveRegistrationId(request);
if (registrationId == null) {
return null;
}
String redirectUriAction = getAction(request, "login");
return resolve(request, registrationId, redirectUriAction);
}
private OAuth2AuthorizationRequest resolve(HttpServletRequest request, String registrationId,
String redirectUriAction) {
if (registrationId == null) {
return null;
}
ClientRegistration clientRegistration = this.clientRegistrationRepository.findByRegistrationId(registrationId);
if (clientRegistration == null) {
throw new InvalidClientRegistrationIdException("Invalid Client Registration with Id: " + registrationId);
}
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest.Builder builder = getBuilder(clientRegistration);
String redirectUriStr = expandRedirectUri(request, clientRegistration, redirectUriAction);
// @formatter:off
builder.clientId(clientRegistration.getClientId())
.authorizationUri(clientRegistration.getProviderDetails().getAuthorizationUri())
.redirectUri(redirectUriStr)
.scopes(clientRegistration.getScopes())
.state(DEFAULT_STATE_GENERATOR.generateKey());
// @formatter:on
this.authorizationRequestCustomizer.accept(builder);
return builder.build();
}
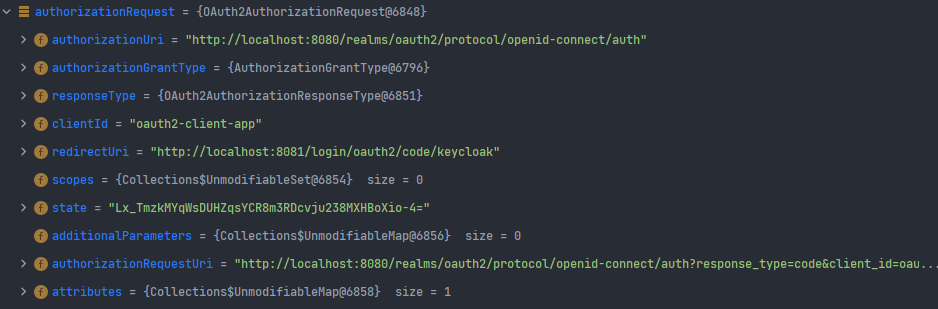
Oauth2AuthorizationRequest
Authorization Code를 요청하는 과정에서 필요한 매개변수를 저장하고 있으며, 이후, 응답을 검증 할때 활용된다
public final class OAuth2AuthorizationRequest implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private String authorizationUri;
private AuthorizationGrantType authorizationGrantType;
private OAuth2AuthorizationResponseType responseType;
private String clientId;
private String redirectUri;
private Set<String> scopes;
private String state;
private Map<String, Object> additionalParameters;
private String authorizationRequestUri;
private Map<String, Object> attributes;
...
}
Oauth2AuthorizationRequestRepository
위의 Oauth2AuthorizationRequest 객체를 저장하고 있는 객체로, 세션 혹은 쿠키에 저장하는 작업을 진행한다.
public interface AuthorizationRequestRepository<T extends OAuth2AuthorizationRequest> {
T loadAuthorizationRequest(HttpServletRequest request);
void saveAuthorizationRequest(T authorizationRequest, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response);
T removeAuthorizationRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response);
}
동작 과정
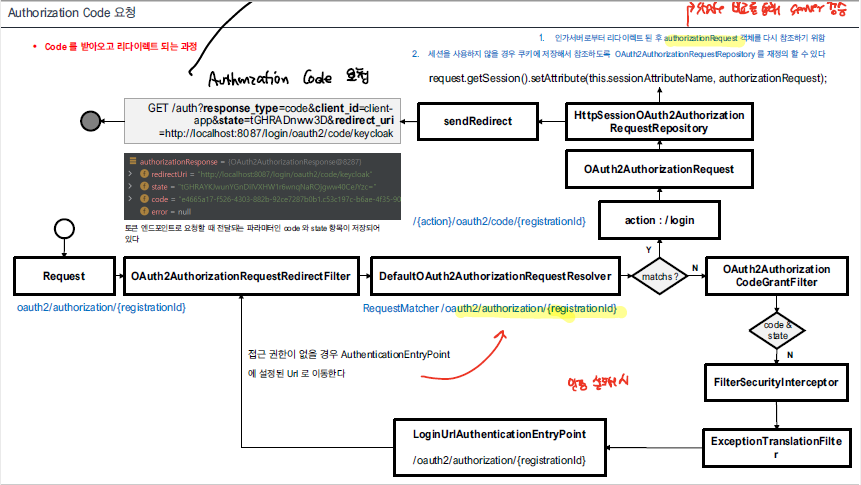
- oauth2/authorization/{registrationId} 요청에 대하며 Oauth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter에서 처리하게 되며, 우선적으로 Oauth2AuthorizationRequestResolver을 통해 Oauth2AuthorizationRequest 객체를 생성한다.
이때, DefaultOauth2AuthorizationRequestResolver 객체가 동작하게 된다.
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = this.authorizationRequestResolver.resolve(request);
if (authorizationRequest != null) {
this.sendRedirectForAuthorization(request, response, authorizationRequest);
return;
}
}
- DefaultOauth2AuthorizationRequestResolver을 통해 Oauth2AuthorizationRequest을 만들어낸다.
- Oauth2AuthorizationRequest 객체를 RequestRepository에 저장한다. HttpSessionOAuth2AuthorizationRequestRepository 객체가 실행되면서, Session에 저장하게 된다.
private void sendRedirectForAuthorization(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest) throws IOException {
if (AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE.equals(authorizationRequest.getGrantType())) {
this.authorizationRequestRepository.saveAuthorizationRequest(authorizationRequest, request, response);
}
...
}
@Override
public void saveAuthorizationRequest(OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
Assert.notNull(request, "request cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(response, "response cannot be null");
if (authorizationRequest == null) {
removeAuthorizationRequest(request, response);
return;
}
String state = authorizationRequest.getState();
Assert.hasText(state, "authorizationRequest.state cannot be empty");
request.getSession().setAttribute(this.sessionAttributeName, authorizationRequest);
}
- sendRedirect 요청으로 Authorization Code를 요청한다.
this.authorizationRedirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response,
authorizationRequest.getAuthorizationRequestUri());
}
@Override
public void sendRedirect(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String url) throws IOException {
String redirectUrl = calculateRedirectUrl(request.getContextPath(), url);
redirectUrl = response.encodeRedirectURL(redirectUrl);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Redirecting to %s", redirectUrl));
}
response.sendRedirect(redirectUrl);
}
아래의 url로 redirect 시키는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
http://localhost:8080/realms/oauth2/protocol/openid-connect/auth?response_type=code&client_id=oauth2-client-app&state=Lx_TmzkMYqWsDUHZqsYCR8m3RDcvju238MXHBoXio-4%3D&redirect_uri=http://localhost:8081/login/oauth2/code/keycloak
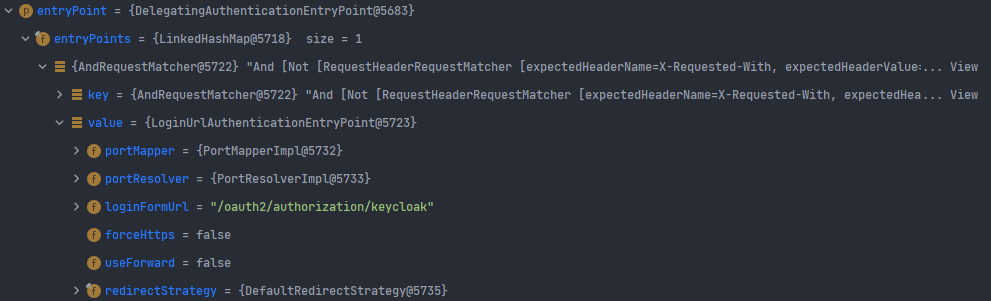
- 인증이 되지 않은 사용자가 만약 다른 경로로 요청을 수행하는 경우 위의 redirect filter을 그냥 통과하게 되면서 이후 authorization filter에 의해 접근이 제한 되게 되면 AuthenticationEntryPoint에 의해 Login Page로 redirect 되게 된다.
Access Token 요청
Access Token은 Oauth2LoginAuthenticationFilter에서 동작한다. 해당 필터에서는 access token 요청, Oauth2AuthorizedClient 생성, Security Context에 Authentication 객체를 저장하는 작업으 수행한다.
주요 클래스
- Oauth2AuthenticationProvider
scope에 openid가 포함되어 있으면 OidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider을 그렇지 않으면 Oauth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider을 호출하여 Token 생성을 위임한다.
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken loginAuthenticationToken = (OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken) authentication;
// Section 3.1.2.1 Authentication Request -
// https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#AuthRequest scope
// REQUIRED. OpenID Connect requests MUST contain the "openid" scope value.
if (loginAuthenticationToken.getAuthorizationExchange().getAuthorizationRequest().getScopes()
.contains("openid")) {
// This is an OpenID Connect Authentication Request so return null
// and let OidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider handle it instead
return null;
}
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationToken authorizationCodeAuthenticationToken;
try {
authorizationCodeAuthenticationToken = (OAuth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationToken) this.authorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider
.authenticate(new OAuth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationToken(
loginAuthenticationToken.getClientRegistration(),
loginAuthenticationToken.getAuthorizationExchange()));
}
- DefaultAuthorizationCodeTokenResponseClient
실제로 Authorization Server으로 부터 Access Token을 얻기 위해 POST 요청을 수행한다.
@Override
public OAuth2AccessTokenResponse getTokenResponse(
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantRequest authorizationCodeGrantRequest) {
Assert.notNull(authorizationCodeGrantRequest, "authorizationCodeGrantRequest cannot be null");
RequestEntity<?> request = this.requestEntityConverter.convert(authorizationCodeGrantRequest);
ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessTokenResponse> response = getResponse(request);
// As per spec, in Section 5.1 Successful Access Token Response
// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-5.1
// If AccessTokenResponse.scope is empty, then we assume all requested scopes were
// granted.
// However, we use the explicit scopes returned in the response (if any).
return response.getBody();
}
private ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessTokenResponse> getResponse(RequestEntity<?> request) {
try {
return this.restOperations.exchange(request, OAuth2AccessTokenResponse.class);
}
catch (RestClientException ex) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(INVALID_TOKEN_RESPONSE_ERROR_CODE,
"An error occurred while attempting to retrieve the OAuth 2.0 Access Token Response: "
+ ex.getMessage(),
null);
throw new OAuth2AuthorizationException(oauth2Error, ex);
}
}
동작 과정
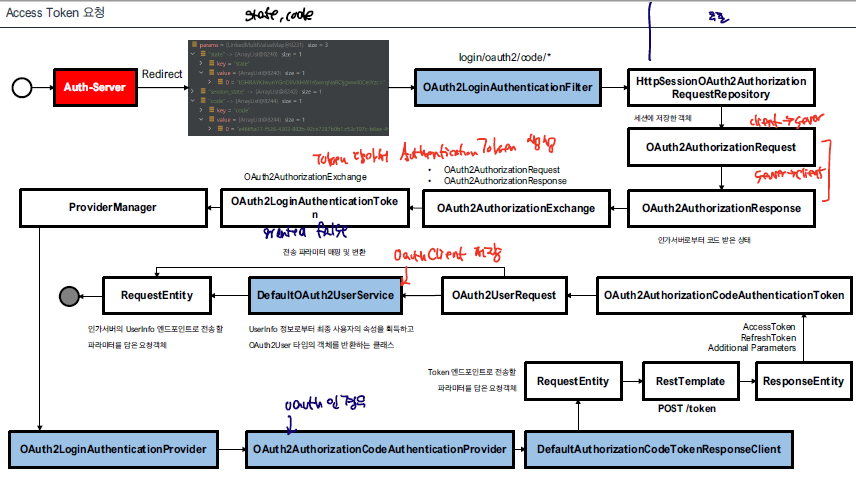
Authorization Code을 요청하고 난 이후에는 설정한 redirect-uri으로 리다이렉트 되는데, Oauth2LoginAuthenticationFilter 이에 대한 요청을 처리한다.
- Oauth2AuthorizationRequest와 Oauth2AuthorizationResponse 객체를 만들어낸다. Oauth2AuthorizationRequest은 세션에 저장되어 있고, Oauth2AuthorizationResponse는 Authorization Server로 부터 응답이다.
if (!OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.isAuthorizationResponse(params)) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(OAuth2ErrorCodes.INVALID_REQUEST);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = this.authorizationRequestRepository
.removeAuthorizationRequest(request, response);
if (authorizationRequest == null) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_NOT_FOUND_ERROR_CODE);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
String registrationId = authorizationRequest.getAttribute(OAuth2ParameterNames.REGISTRATION_ID);
ClientRegistration clientRegistration = this.clientRegistrationRepository.findByRegistrationId(registrationId);
if (clientRegistration == null) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(CLIENT_REGISTRATION_NOT_FOUND_ERROR_CODE,
"Client Registration not found with Id: " + registrationId, null);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
// @formatter:off
String redirectUri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(UrlUtils.buildFullRequestUrl(request))
.replaceQuery(null)
.build()
.toUriString();
// @formatter:on
OAuth2AuthorizationResponse authorizationResponse = OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.convert(params,
redirectUri);
- 해당 객체들을 Oauth2AuthorizationExchange 객체에 넣어서 Oauth2LoginAuthenticationToken을 만든다.
인증이 완료되고 나면 Oauth2LoginAuthenticationToken에 User principal 과 각종 Token이 저장된다.
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationRequest = new OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken(clientRegistration,
new OAuth2AuthorizationExchange(authorizationRequest, authorizationResponse));
authenticationRequest.setDetails(authenticationDetails);
public class OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private OAuth2User principal;
private ClientRegistration clientRegistration;
private OAuth2AuthorizationExchange authorizationExchange;
private OAuth2AccessToken accessToken;
private OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken;
...
}
- Oauth2LoginAuthenticationToken을 ProviderManager에 전달하고, Oauth2LoginAuthenticationProvider -> Oauth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider을 호출한다.
해당 provider 내부에 보면 Oauth2AuthorizationRequest와 Oauth2AuthorizationResponse의 state 값을 비교해서 틀리면, 인증을 요청을 처리하지 않는 로직도 확인할 수 있다.
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = (OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken) this
.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authenticationRequest);
//Oauth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationToken authorizationCodeAuthentication = (OAuth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationToken) authentication;
OAuth2AuthorizationResponse authorizationResponse = authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange()
.getAuthorizationResponse();
if (authorizationResponse.statusError()) {
throw new OAuth2AuthorizationException(authorizationResponse.getError());
}
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange()
.getAuthorizationRequest();
if (!authorizationResponse.getState().equals(authorizationRequest.getState())) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(INVALID_STATE_PARAMETER_ERROR_CODE);
throw new OAuth2AuthorizationException(oauth2Error);
}
OAuth2AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = this.accessTokenResponseClient.getTokenResponse(
new OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantRequest(authorizationCodeAuthentication.getClientRegistration(),
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange()));
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new OAuth2AuthorizationCodeAuthenticationToken(
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getClientRegistration(),
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange(), accessTokenResponse.getAccessToken(),
accessTokenResponse.getRefreshToken(), accessTokenResponse.getAdditionalParameters());
authenticationResult.setDetails(authorizationCodeAuthentication.getDetails());
return authenticationResult;
}
- DefaultAuthorizationCodeTokenResponseClient 요청으로 실제 Access Token을 요청하는 작업을 진행한다.
OAuth2AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse = this.accessTokenResponseClient.getTokenResponse(
new OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantRequest(authorizationCodeAuthentication.getClientRegistration(),
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange()));
@Override
public OAuth2AccessTokenResponse getTokenResponse(
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantRequest authorizationCodeGrantRequest) {
Assert.notNull(authorizationCodeGrantRequest, "authorizationCodeGrantRequest cannot be null");
RequestEntity<?> request = this.requestEntityConverter.convert(authorizationCodeGrantRequest);
ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessTokenResponse> response = getResponse(request);
// As per spec, in Section 5.1 Successful Access Token Response
// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-5.1
// If AccessTokenResponse.scope is empty, then we assume all requested scopes were
// granted.
// However, we use the explicit scopes returned in the response (if any).
return response.getBody();
}
private ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessTokenResponse> getResponse(RequestEntity<?> request) {
try {
return this.restOperations.exchange(request, OAuth2AccessTokenResponse.class);
}
catch (RestClientException ex) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(INVALID_TOKEN_RESPONSE_ERROR_CODE,
"An error occurred while attempting to retrieve the OAuth 2.0 Access Token Response: "
+ ex.getMessage(),
null);
throw new OAuth2AuthorizationException(oauth2Error, ex);
}
}
위의 로직을 통해 아래의 AccessTokenResponse 객체가 초기화되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
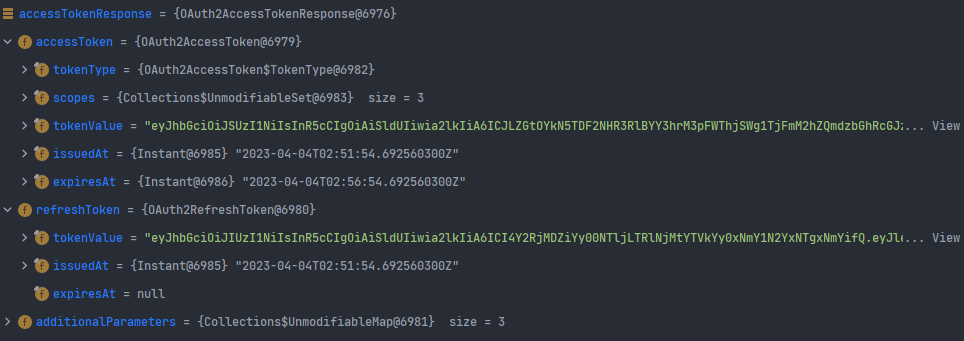
- 인증이 완료된 이후, OauthAuthorizedClient을 만들어내는 작업을 진행한다. Oauth2AuthorizedClient에는 user principal, 각종 token이 저장되어 Spring Framework 내부에서 언제든지 활용할 수 있다.
OAuth2AuthenticationToken oauth2Authentication = this.authenticationResultConverter
.convert(authenticationResult);
Assert.notNull(oauth2Authentication, "authentication result cannot be null");
oauth2Authentication.setDetails(authenticationDetails);
OAuth2AuthorizedClient authorizedClient = new OAuth2AuthorizedClient(
authenticationResult.getClientRegistration(), oauth2Authentication.getName(),
authenticationResult.getAccessToken(), authenticationResult.getRefreshToken());
this.authorizedClientRepository.saveAuthorizedClient(authorizedClient, oauth2Authentication, request, response);
public class OAuth2AuthorizedClient implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private final ClientRegistration clientRegistration;
private final String principalName;
private final OAuth2AccessToken accessToken;
private final OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken;
...
}
User Model
위의 인증 과정을 통해 생성한 Access Token을 활용하여 UserInfo을 요청할 수 있다. UserInfo를 요청하여 Spring 내부에서 OAuth2User 타입의 객체로 형태로 유저를 관리하게 되는데, 이때 2가지 타입이 존재한다.
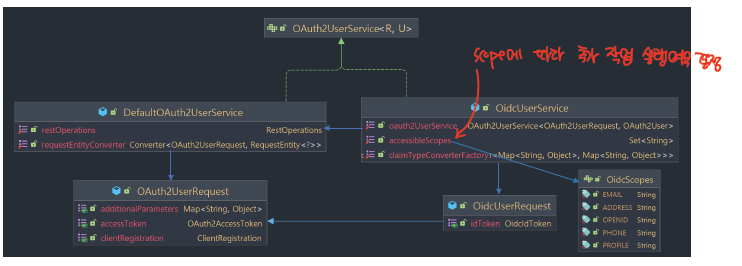
위의 구조를 보면 알듯이 OidcUser는 OAuth2User을 상속하는 형태로 이루어져 있어, OAuth2User 객체를 통한 통합 관리가 가능하다.
DefaultOAuth2UserService
표준 OAuth2 Prodiver 인증 방식으로 OAuth2User 유저를 활용하여 관리하게 된다.
OidcUserService
OIDC 기반의 인증을 통해 OidcUser 타입의 객체를 관리하게 된다.
각각의 인증방식에서 동작하는 provider 내부에서 아래와 같이 loadUser를 호출하여 각각에 맞는 유저 타입을 관리하게 된다.
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
...
OAuth2User oauth2User = this.userService.loadUser(new OAuth2UserRequest(
loginAuthenticationToken.getClientRegistration(), accessToken, additionalParameters));
...
}
OAuth2User
OAuth2User 내부에는 사용자에 대한 정보를 저장하기 위해 attributes, authorities와 같은 필드를 가지로 있다.
public class DefaultOAuth2User implements OAuth2User, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
private final Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities;
private final Map<String, Object> attributes;
private final String nameAttributeKey;
...
}
OAuth2 Provider 기반의 인증을 통해 OAuth2User 객체를 생성하는 과정을 알아보자
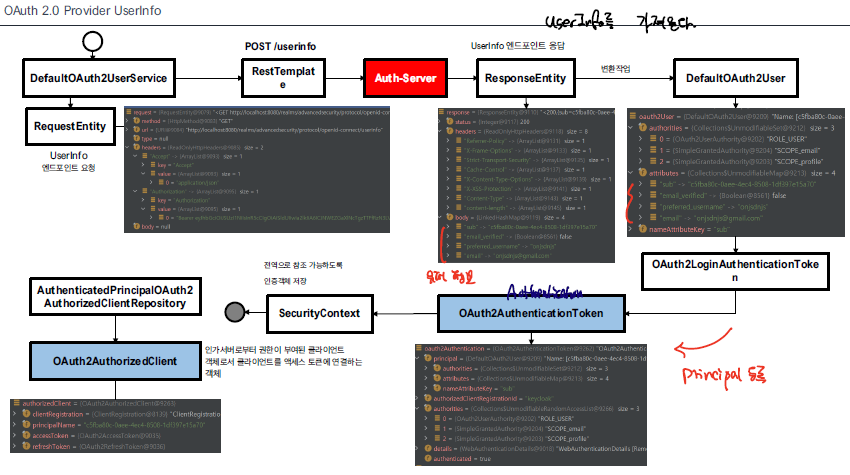
- provider에 의해 loadUser이 호출된다.
OAuth2User oauth2User = this.userService.loadUser(new OAuth2UserRequest(
loginAuthenticationToken.getClientRegistration(), accessToken, additionalParameters));
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> mappedAuthorities = this.authoritiesMapper
.mapAuthorities(oauth2User.getAuthorities());
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken(
loginAuthenticationToken.getClientRegistration(), loginAuthenticationToken.getAuthorizationExchange(),
oauth2User, mappedAuthorities, accessToken, authorizationCodeAuthenticationToken.getRefreshToken());
authenticationResult.setDetails(loginAuthenticationToken.getDetails());
return authenticationResult;
- OAuth2UserRequest 객체를 RequestEntity로 변환하여 UserInfo에 대한 요청을 수행한다.
@Override
public OAuth2User loadUser(OAuth2UserRequest userRequest) throws OAuth2AuthenticationException {
Assert.notNull(userRequest, "userRequest cannot be null");
if (!StringUtils
.hasText(userRequest.getClientRegistration().getProviderDetails().getUserInfoEndpoint().getUri())) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(MISSING_USER_INFO_URI_ERROR_CODE,
"Missing required UserInfo Uri in UserInfoEndpoint for Client Registration: "
+ userRequest.getClientRegistration().getRegistrationId(),
null);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
String userNameAttributeName = userRequest.getClientRegistration().getProviderDetails().getUserInfoEndpoint()
.getUserNameAttributeName();
if (!StringUtils.hasText(userNameAttributeName)) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(MISSING_USER_NAME_ATTRIBUTE_ERROR_CODE,
"Missing required \"user name\" attribute name in UserInfoEndpoint for Client Registration: "
+ userRequest.getClientRegistration().getRegistrationId(),
null);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
RequestEntity<?> request = this.requestEntityConverter.convert(userRequest);
ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> response = getResponse(userRequest, request);
- ResponseEntity를 전달받은 이후에는 이를 DefaultOAuth2User로 생성한다.
Map<String, Object> userAttributes = response.getBody();
Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new LinkedHashSet<>();
authorities.add(new OAuth2UserAuthority(userAttributes));
OAuth2AccessToken token = userRequest.getAccessToken();
for (String authority : token.getScopes()) {
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("SCOPE_" + authority));
}
return new DefaultOAuth2User(authorities, userAttributes, userNameAttributeName);
}
- 이후 OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken를 구성하여 이를 SecurityContext에 저장하는 작업을 수행한다.
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
...
OAuth2User oauth2User = this.userService.loadUser(new OAuth2UserRequest(
loginAuthenticationToken.getClientRegistration(), accessToken, additionalParameters));
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> mappedAuthorities = this.authoritiesMapper
.mapAuthorities(oauth2User.getAuthorities());
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken(
loginAuthenticationToken.getClientRegistration(), loginAuthenticationToken.getAuthorizationExchange(),
oauth2User, mappedAuthorities, accessToken, authorizationCodeAuthenticationToken.getRefreshToken());
authenticationResult.setDetails(loginAuthenticationToken.getDetails());
return authenticationResult;
}
OidcUser
Oidc User는 OpenId Connect 기반의 인증을 통해 생성되는 유저 객체로, scope에 openid가 포함된 경우 동작하게 된다. OAuth2User와 달리 OidcIdToken과 OidcUserInfo 객체를 가지고 있는것이 특징이다.
public class DefaultOidcUser extends DefaultOAuth2User implements OidcUser {
private final OidcIdToken idToken;
private final OidcUserInfo userInfo;
OidcUser 객체를 생성하는 작업을 살펴보자
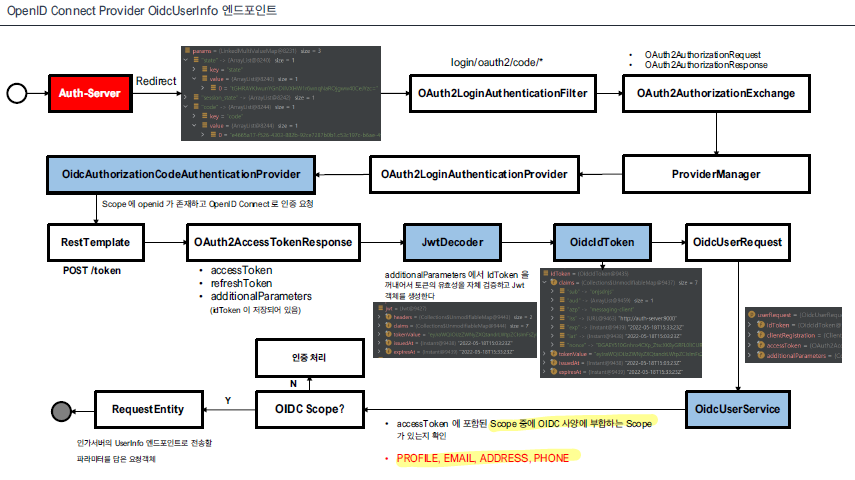
- provider에서 IdToken을 생성하는 작업을 수행한다.
IdToken을 생성하는 과정에서 JwtDecoder을 활용하여 검증을 수행하게 된다.
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
...
OidcIdToken idToken = createOidcToken(clientRegistration, accessTokenResponse);
}
private OidcIdToken createOidcToken(ClientRegistration clientRegistration,
OAuth2AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse) {
JwtDecoder jwtDecoder = this.jwtDecoderFactory.createDecoder(clientRegistration);
Jwt jwt = getJwt(accessTokenResponse, jwtDecoder);
OidcIdToken idToken = new OidcIdToken(jwt.getTokenValue(), jwt.getIssuedAt(), jwt.getExpiresAt(),
jwt.getClaims());
return idToken;
}
private Jwt getJwt(OAuth2AccessTokenResponse accessTokenResponse, JwtDecoder jwtDecoder) {
try {
Map<String, Object> parameters = accessTokenResponse.getAdditionalParameters();
return jwtDecoder.decode((String) parameters.get(OidcParameterNames.ID_TOKEN));
}
catch (JwtException ex) {
OAuth2Error invalidIdTokenError = new OAuth2Error(INVALID_ID_TOKEN_ERROR_CODE, ex.getMessage(), null);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(invalidIdTokenError, invalidIdTokenError.toString(), ex);
}
}
- loadUser가 호출되어 OidcUser 객체를 반환하게 된다.
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
...
OidcUser oidcUser = this.userService.loadUser(new OidcUserRequest(clientRegistration,
accessTokenResponse.getAccessToken(), idToken, additionalParameters));
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> mappedAuthorities = this.authoritiesMapper
.mapAuthorities(oidcUser.getAuthorities());
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken(
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getClientRegistration(),
authorizationCodeAuthentication.getAuthorizationExchange(), oidcUser, mappedAuthorities,
accessTokenResponse.getAccessToken(), accessTokenResponse.getRefreshToken());
authenticationResult.setDetails(authorizationCodeAuthentication.getDetails());
return authenticationResult;
}
@Override
public OidcUser loadUser(OidcUserRequest userRequest) throws OAuth2AuthenticationException {
Assert.notNull(userRequest, "userRequest cannot be null");
OidcUserInfo userInfo = null;
if (this.shouldRetrieveUserInfo(userRequest)) {
OAuth2User oauth2User = this.oauth2UserService.loadUser(userRequest);
Map<String, Object> claims = getClaims(userRequest, oauth2User);
userInfo = new OidcUserInfo(claims);
// https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#UserInfoResponse
// 1) The sub (subject) Claim MUST always be returned in the UserInfo Response
if (userInfo.getSubject() == null) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(INVALID_USER_INFO_RESPONSE_ERROR_CODE);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
// 2) Due to the possibility of token substitution attacks (see Section
// 16.11),
// the UserInfo Response is not guaranteed to be about the End-User
// identified by the sub (subject) element of the ID Token.
// The sub Claim in the UserInfo Response MUST be verified to exactly match
// the sub Claim in the ID Token; if they do not match,
// the UserInfo Response values MUST NOT be used.
if (!userInfo.getSubject().equals(userRequest.getIdToken().getSubject())) {
OAuth2Error oauth2Error = new OAuth2Error(INVALID_USER_INFO_RESPONSE_ERROR_CODE);
throw new OAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());
}
}
Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new LinkedHashSet<>();
authorities.add(new OidcUserAuthority(userRequest.getIdToken(), userInfo));
OAuth2AccessToken token = userRequest.getAccessToken();
for (String authority : token.getScopes()) {
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("SCOPE_" + authority));
}
return getUser(userRequest, userInfo, authorities);
}
이때, OidcUserRequest에 설정된 scope에 따라 동작이 조금 달라지게 된다. 아래의 메소드의 반환 결과에 따라 UserInfo를 요청하는 작업이 수행되거나, 그렇지 않게 된다.
Scope 중에 Profile, Email, Address, Phone이 포함된 경우에는 아래의 메소드에 True를 반환하게 되어 유저 정보를 요청하는 작업을 수행하여 OidcUserInfo 객체를 생성하는 과정이 이루어진다.
private Set<String> accessibleScopes = new HashSet<>(
Arrays.asList(OidcScopes.PROFILE, OidcScopes.EMAIL, OidcScopes.ADDRESS, OidcScopes.PHONE));
private boolean shouldRetrieveUserInfo(OidcUserRequest userRequest) {
// Auto-disabled if UserInfo Endpoint URI is not provided
ProviderDetails providerDetails = userRequest.getClientRegistration().getProviderDetails();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(providerDetails.getUserInfoEndpoint().getUri())) {
return false;
}
// The Claims requested by the profile, email, address, and phone scope values
// are returned from the UserInfo Endpoint (as described in Section 5.3.2),
// when a response_type value is used that results in an Access Token being
// issued.
// However, when no Access Token is issued, which is the case for the
// response_type=id_token,
// the resulting Claims are returned in the ID Token.
// The Authorization Code Grant Flow, which is response_type=code, results in an
// Access Token being issued.
if (AuthorizationGrantType.AUTHORIZATION_CODE
.equals(userRequest.getClientRegistration().getAuthorizationGrantType())) {
// Return true if there is at least one match between the authorized scope(s)
// and accessible scope(s)
//
// Also return true if authorized scope(s) is empty, because the provider has
// not indicated which scopes are accessible via the access token
// @formatter:off
return this.accessibleScopes.isEmpty()
|| CollectionUtils.isEmpty(userRequest.getAccessToken().getScopes())
|| CollectionUtils.containsAny(userRequest.getAccessToken().getScopes(), this.accessibleScopes);
// @formatter:on
}
return false;
}
이후의 작업에 대해서는 위의 DefaultOAuth2User와 동일한 방식으로 동작하게 된다.
OpenId Connect Logout
OIDC 인증을 통해 로그인을 성공한 유저에 대한 로그아웃 과정은 아래와 같이 이루어진다.
- 세션, 쿠키 삭제
- OidcClientInitiatedLogoutSuccessHandler을 통한 서버 로그아웃 요청
- 로그아웃 이후에 사용자를 redirect 시킨다.
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
...
httpSecurity.logout()
.logoutSuccessHandler(oidcLogoutSuccessHandler())
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
.clearAuthentication(true)
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID");
return httpSecurity.build();
}
private LogoutSuccessHandler oidcLogoutSuccessHandler() {
OidcClientInitiatedLogoutSuccessHandler successHandler = new OidcClientInitiatedLogoutSuccessHandler(clientRegistrationRepository);
successHandler.setPostLogoutRedirectUri("http://localhost:8081/login");
return successHandler;
}
OidcClientInitiatedLogoutSuccessHandler 객체 내부에서 ClientRegistration에 등록된 정보를 토대로 Logout Url를 구성하고 필요한 parameter을 처리한 다음에 targetUrl를 생성하고 해당 url로 요청을 전달하여 로그아웃을 수행한다.
Spring MVC 인증 객체 접근
Spring MVC 기반의 Controller을 구성하는 경우 아래와 같이 Parameter을 설정하여 인증 객체에 대한 접근이 가능하다. 이를 가능하게 해주는 것이 AuthenticationPrincipalArgumentResolver에 의해 각종 인자들이 제공된다.
@GetMapping("/user")
public OAuth2User user(Authentication authentication) {
OAuth2AuthenticationToken authentication1 = (OAuth2AuthenticationToken) authentication;
OAuth2AuthenticationToken authentication2 = (OAuth2AuthenticationToken) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
OAuth2User oAuth2User1 = authentication1.getPrincipal();
OAuth2User oAuth2User2 = authentication2.getPrincipal();
return oAuth2User2;
}
@GetMapping("/oauth2User")
public OAuth2User oAuth2User(@AuthenticationPrincipal OAuth2User oAuth2User) {
return oAuth2User;
}
@GetMapping("/oidcUser")
public OidcUser oidcUser(@AuthenticationPrincipal OidcUser oidcUser) {
return oidcUser;
}
CustomApi 설정
Endpoint 수정
Oauth2 dependency 추가만으로 Oauth2 기반의 인증이 자동을 수행되고, default로 설정된 endpoint에 따라 요청을 처리하게 되지만, 정책상 endpoint을 다르게 설정해야하는 경우가 있는데, 이때 각종 endpoint에 대한 설정을 수정할 수 있다.
아래와 같이 AuthorizationEndpoint, RedirectionEndpoint을 수정하는 것이 가능하다. 이렇게 설정을 바꾸게 되면 각종 filter에 등록된 requestmatcher 또한 자동으로 수정되어 수정된 endpoint에 대한 요청을 처리할 수 있도록 한다.
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity.authorizeHttpRequests()
.requestMatchers("/login").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
httpSecurity.oauth2Login(
oauth2-> oauth2.loginPage("/login")
.authorizationEndpoint(authorizationEndpointConfig -> authorizationEndpointConfig.baseUri("/oauth2/v1/authorization"))
.redirectionEndpoint(redirectionEndpointConfig -> redirectionEndpointConfig.baseUri("/login/v1/oauth2/code/*"))
);
}
추가로, RedirectionEnpoint에 대한 수정을 하는 경우 Authorization Server에 설정된 Redirect Url도 같이 수정해야 정상적인 동작이 수행된다.
Oauth2AuthoricationRequestResolver
Authorization Code을 요청하는 과정에서 Oauth2AuthorizationRequest을 생성하는 작업을 수행하게 된다.
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest = this.authorizationRequestResolver.resolve(request);
if (authorizationRequest != null) {
this.sendRedirectForAuthorization(request, response, authorizationRequest);
return;
}
}
...
}
}
@Override
public OAuth2AuthorizationRequest resolve(HttpServletRequest request) {
String registrationId = resolveRegistrationId(request);
if (registrationId == null) {
return null;
}
String redirectUriAction = getAction(request, "login");
return resolve(request, registrationId, redirectUriAction);
}
@Override
public OAuth2AuthorizationRequest resolve(HttpServletRequest request, String registrationId) {
if (registrationId == null) {
return null;
}
String redirectUriAction = getAction(request, "authorize");
return resolve(request, registrationId, redirectUriAction);
}
private String getAction(HttpServletRequest request, String defaultAction) {
String action = request.getParameter("action");
if (action == null) {
return defaultAction;
}
return action;
}
private OAuth2AuthorizationRequest resolve(HttpServletRequest request, String registrationId,
String redirectUriAction) {
if (registrationId == null) {
return null;
}
ClientRegistration clientRegistration = this.clientRegistrationRepository.findByRegistrationId(registrationId);
if (clientRegistration == null) {
throw new InvalidClientRegistrationIdException("Invalid Client Registration with Id: " + registrationId);
}
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest.Builder builder = getBuilder(clientRegistration);
String redirectUriStr = expandRedirectUri(request, clientRegistration, redirectUriAction);
// @formatter:off
builder.clientId(clientRegistration.getClientId())
.authorizationUri(clientRegistration.getProviderDetails().getAuthorizationUri())
.redirectUri(redirectUriStr)
.scopes(clientRegistration.getScopes())
.state(DEFAULT_STATE_GENERATOR.generateKey());
// @formatter:on
this.authorizationRequestCustomizer.accept(builder);
return builder.build();
}
만약, 아래와 같이 Authorization Code 방식에서 PKCE을 적용하고자 하는 경우 어떻게 될까? Authorization Server에서 PKCE 설정을 처리한 후에 진행한다.
keycloakWithPKCE:
clientId: oauth2-client-app2
clientSecret: NA7bQuB4IqTGQMgxCdPNi8CUgx6kXLwO
redirectUri: http://localhost:8081/login/oauth2/code/keycloak
authorizationGrantType: authorization_code
clientName: oauth2-client-app
clientAuthenticationMethod: client_secret_post
scope: openid, profile
provider: keycloak
이는, Spring에서 기본으로 설정되어 있는 로직이 아래와 같이 ClientAuthenticationMethod이 None으로 설정되야 PKCE가 적용되기 때문이다.
private OAuth2AuthorizationRequest.Builder getBuilder(ClientRegistration clientRegistration) {
...
if (ClientAuthenticationMethod.NONE.equals(clientRegistration.getClientAuthenticationMethod())) {
DEFAULT_PKCE_APPLIER.accept(builder);
}
return builder;
...
}
그러면 아래와 같이 ClientAuthenticationMethod을 None으로 설정해보자
keycloakWithPKCE:
clientId: oauth2-client-app2
clientSecret: NA7bQuB4IqTGQMgxCdPNi8CUgx6kXLwO
redirectUri: http://localhost:8081/login/oauth2/code/keycloak
authorizationGrantType: authorization_code
clientName: oauth2-client-app
clientAuthenticationMethod: none
scope: openid, profile
provider: keycloak
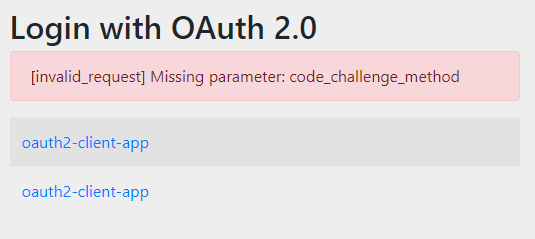
요청을 수행해보면 아래와 같은 에러가 발생하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이는, client-secret이 전달되지 않아 발생하는 문제이다. 따라서, Spring Security에서 기본으로 동작하는 과정에서는 Authorization Code + PKCE 방식을 적용할 수 없다. 이를 위해 아래와 같이 ArgumentResolver을 직접 구현하여 필요한 로직을 처리한다.
CustomOAuth2AuthorizationRequestResolver
public class CustomOAuth2AuthorizationRequestResolver implements OAuth2AuthorizationRequestResolver {
private static final String REGISTRATION_ID_URI_VARIABLE_NAME = "registrationId";
private ClientRegistrationRepository clientRegistrationRepository;
private String baseUri;
private AntPathRequestMatcher authorizationRequestMatcher;
private DefaultOAuth2AuthorizationRequestResolver defaultResolver;
private static final Consumer<OAuth2AuthorizationRequest.Builder> DEFAULT_PKCE_APPLIER = OAuth2AuthorizationRequestCustomizers
.withPkce();
public CustomOAuth2AuthorizationRequestResolver(ClientRegistrationRepository clientRegistrationRepository, String baseUri) {
this.clientRegistrationRepository = clientRegistrationRepository;
this.baseUri = baseUri;
this.authorizationRequestMatcher = new AntPathRequestMatcher(baseUri + "/{" + REGISTRATION_ID_URI_VARIABLE_NAME + "}");
defaultResolver = new DefaultOAuth2AuthorizationRequestResolver(clientRegistrationRepository, baseUri);
}
@Override
public OAuth2AuthorizationRequest resolve(HttpServletRequest request) {
String registrationId = resolveRegistrationId(request);
if (registrationId == null) {
return null;
}
if(registrationId.equals("keycloakWithPKCE")){
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest oAuth2AuthorizationRequest = defaultResolver.resolve(request);
ClientRegistration clientRegistration = clientRegistrationRepository.findByRegistrationId(registrationId);
return customResolve(oAuth2AuthorizationRequest,registrationId);
}
return defaultResolver.resolve(request);
}
@Override
public OAuth2AuthorizationRequest resolve(HttpServletRequest request, String registrationId) {
if (registrationId == null) {
return null;
}
if(registrationId.equals("keycloakWithPKCE")){
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest oAuth2AuthorizationRequest = defaultResolver.resolve(request);
ClientRegistration clientRegistration = clientRegistrationRepository.findByRegistrationId(registrationId);
return customResolve(oAuth2AuthorizationRequest,registrationId);
}
return defaultResolver.resolve(request);
}
private OAuth2AuthorizationRequest customResolve(OAuth2AuthorizationRequest oAuth2AuthorizationRequest, String clientRegistrationId) {
Map<String,Object> extraParams = new HashMap<>();
extraParams.put("customName1","customValue1");
extraParams.put("customName2","customValue2");
extraParams.put("customName3","customValue3");
extraParams.put("customName4","customValue4");
OAuth2AuthorizationRequest.Builder builder = OAuth2AuthorizationRequest.from(oAuth2AuthorizationRequest);
builder.additionalParameters(extraParams);
DEFAULT_PKCE_APPLIER.accept(builder);
return builder.build();
}
private String resolveRegistrationId(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.authorizationRequestMatcher.matches(request)) {
return this.authorizationRequestMatcher.matcher(request).getVariables()
.get(REGISTRATION_ID_URI_VARIABLE_NAME);
}
return null;
}
}
References
link: inflearn
docs: spring_security

댓글남기기