Spring Security Part 4
SecurityContext, Authentication, Authorization
Security Context
사용자에 대한 인증을 수행하고 나면, Authentication 객체가 생성되어 SecurityContext에 저장되게 된다. 해당 SecurityContext는 ThreadLocal에 저장되어 thread가 실행되는 동안 어플리케이션 전반에서 Authentication 참조가 가능하다.
Authentication authentication=SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()
SecurityContextHolder Strategy
| strategy | description |
|---|---|
| MODE_THREAD_LOCAL | ThreadLocal SecurityContext을 저장한다. |
| MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL | 메인 쓰레드와 공유되는 자식 쓰레드에 대해서 동일한 SecurityContext 유지 |
| MODE_GLOBAL | 어플리케이션 전바에서 하나의 SecurityContext 공유 |
MODE_THREAD_LOCAL로 설정하게 되면 아래와 같이 ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy 클래스가 동작하게 되며, 해당 클래스의 내부를 살펴보면 ThreadLocal에 SecurityContext을 저장하고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy
final class ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy implements SecurityContextHolderStrategy {
private static final ThreadLocal<Supplier<SecurityContext>> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Override
public void clearContext() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
@Override
public SecurityContext getContext() {
return getDeferredContext().get();
}
@Override
public Supplier<SecurityContext> getDeferredContext() {
Supplier<SecurityContext> result = contextHolder.get();
if (result == null) {
SecurityContext context = createEmptyContext();
result = () -> context;
contextHolder.set(result);
}
return result;
}
@Override
public void setContext(SecurityContext context) {
Assert.notNull(context, "Only non-null SecurityContext instances are permitted");
contextHolder.set(() -> context);
}
@Override
public void setDeferredContext(Supplier<SecurityContext> deferredContext) {
Assert.notNull(deferredContext, "Only non-null Supplier instances are permitted");
Supplier<SecurityContext> notNullDeferredContext = () -> {
SecurityContext result = deferredContext.get();
Assert.notNull(result, "A Supplier<SecurityContext> returned null and is not allowed.");
return result;
};
contextHolder.set(notNullDeferredContext);
}
@Override
public SecurityContext createEmptyContext() {
return new SecurityContextImpl();
}
}
SecurityContextHolderFilter
실제로 SecurityContext을 생성, 저장, 조회를 담당하는 필터로, 여러 filter에서 해당 Filter을 호출하여 Authentication 객체를 저장한다.
- 익명 사용자 인증시
- AnonymousAuthenticationFilter에서 AnonymousAuthenticationToken을 저장하게 위해 아래와 같이 security context을 저장하게 된다.
@Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { Supplier<SecurityContext> deferredContext = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getDeferredContext(); this.securityContextHolderStrategy .setDeferredContext(defaultWithAnonymous((HttpServletRequest) req, deferredContext)); chain.doFilter(req, res); }
- AnonymousAuthenticationFilter에서 AnonymousAuthenticationToken을 저장하게 위해 아래와 같이 security context을 저장하게 된다.
- 인증 사용자 인증시
- AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter에서는 인증을 수행하고 만들어진 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 저장한다.
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException { SecurityContext context = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext(); context.setAuthentication(authResult); this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setContext(context); this.securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Set SecurityContextHolder to %s", authResult)); } this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult); if (this.eventPublisher != null) { this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(authResult, this.getClass())); } this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult); } - 추후 인증이 완료된 사용자에 된 접속 시도 시
- Session에서 저장된 SecurityContext을 받아서 SecurityContextHoler에 저장한다.
SecurityContextHolderFilter
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException { if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) { chain.doFilter(request, response); return; } request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE); Supplier<SecurityContext> deferredContext = this.securityContextRepository.loadDeferredContext(request); try { this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setDeferredContext(deferredContext); chain.doFilter(request, response); } finally { this.securityContextHolderStrategy.clearContext(); request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED); } }HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository
@Override public SecurityContext loadContext(HttpRequestResponseHolder requestResponseHolder) { HttpServletRequest request = requestResponseHolder.getRequest(); HttpServletResponse response = requestResponseHolder.getResponse(); HttpSession httpSession = request.getSession(false); SecurityContext context = readSecurityContextFromSession(httpSession); if (context == null) { context = generateNewContext(); if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Created %s", context)); } } if (response != null) { SaveToSessionResponseWrapper wrappedResponse = new SaveToSessionResponseWrapper(response, request, httpSession != null, context); wrappedResponse.setSecurityContextHolderStrategy(this.securityContextHolderStrategy); requestResponseHolder.setResponse(wrappedResponse); requestResponseHolder.setRequest(new SaveToSessionRequestWrapper(request, wrappedResponse)); } return context; }
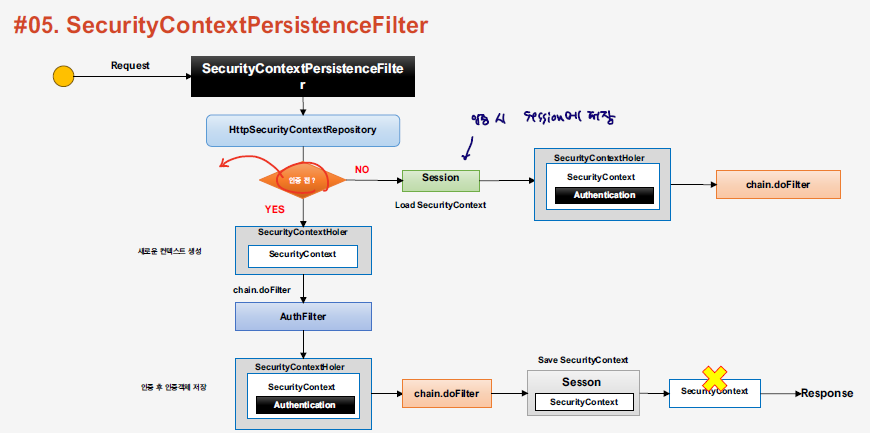
SecurityContextHolderFilter 내부에는 SecurityContextRepository가 동작하게 되면서 실제적인 SecurityContext 객체에 대한 처리를 진행한다.
Authentication
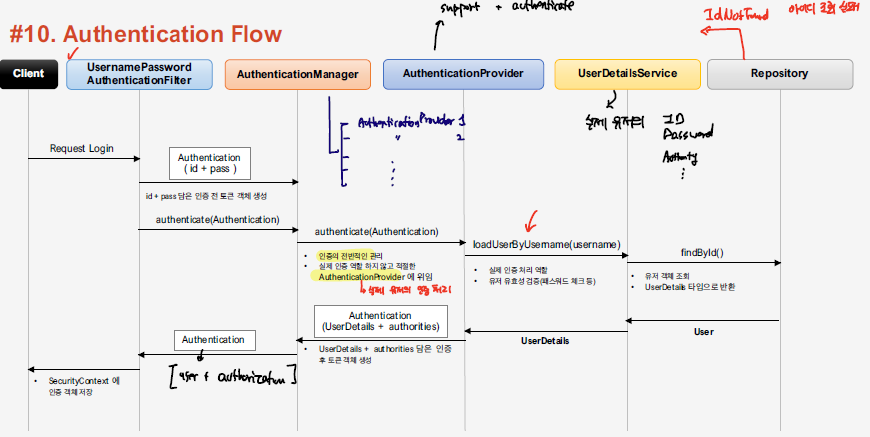
Authentication은 과 같은 흐름으로 동작한다.
AuthenticationManager
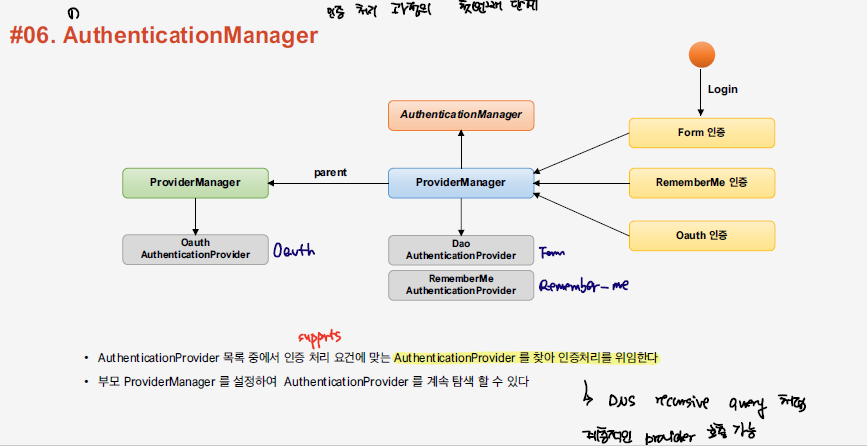
인증 과정의 첫번째 단계로 AuthenticationManager가 동작하게 된다. Authentication 객체를 전달받은 AuthenticationManager은 AuthenticationProvider로 인증을 위임하게 된다.
- FormLogin을 통한 인증방식이 설정되어 있는 경우,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에서 Authentication 객체를 생성해서 이를 AuthenticaionManager로 전달한다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
username = (username != null) ? username.trim() : "";
String password = obtainPassword(request);
password = (password != null) ? password : "";
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username,
password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
- AuthenticationManager을 담당하는 ProviderManager로 호출되면서 해당 인증을 처리할 수 있는 Provider을 호출하면 인증을 수행한다.
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
...
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
parentResult = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
result = parentResult;
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException ex) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
parentException = ex;
lastException = ex;
}
}
return result;
...
}
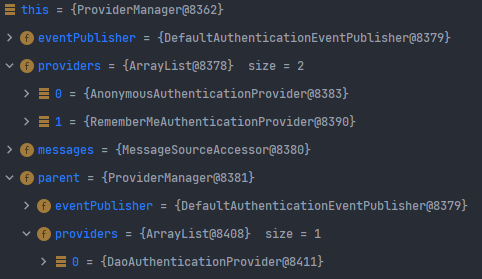
AuthenticationManager의 내부 동작과정을 보면, 여러 개의 Provider 객체를 검사하면서, 해당 인증을 처리할 수 있는 provider을 호출하는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 또한, ProviderManger에 대한 계층이 나타나있으며, 해당 ProviderManager에서 처리할 수 없는 인증 로직에 대해서는 현재 ProviderManager의 parent 객체를 호출하여 이를 처리할 수 있는 Provider가 있는 지 검사한다.
FormLogic의 경우 DaoAuthenticationProvider가 동작한다.
AuthenticationProvider
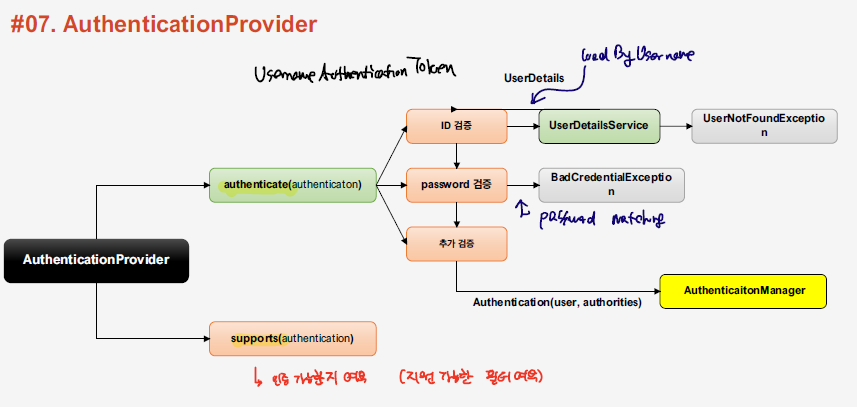
실제로 사용자에 대한 인증을 처리하는 로직은 AuthenticationProvider에서 담당하게 된다. AuthenticationProvider interface를 보면, 아래와 같이, authenticate, supports 메소드가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다. supports을 통해 해당 인증을 처리할 수 있는 여부를 검사하고, authenticate를 이용해서 인증을 처리한다.
AuthenticationProvider
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
Form Login을 처리하는 DaoAuthenticationProvider의 경우 아래와 같이 동작한다.
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
}
Authorization
인증이 완료되면, 특정 자원에 대한 접근 권한이 있는지 확인한다. 이 과정을, Authorization 처리하고 한다.
Spring Security에서는 크게 3단계의 접근 권한을 설정할 수 있다.
| Layer | Description |
| 웹 | url 경로 단위 |
| 서비스 | method 단위 |
| 도메인 | 객체 단위 |
Spring Security의 마지막에 동작하는 filter인 Authorization Filter은 요청에 대해 최종적으로 허용/거부 여부를 결정하게 되는데, 경우에 따라서 인증이 실패한 경우에는 AuthenticationException, 인가가 실패한 경우 AccessDeniedException을 발생한다.
AuthorizationFilter
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String alreadyFilteredAttributeName = getAlreadyFilteredAttributeName();
request.setAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName, Boolean.TRUE);
try {
AuthorizationDecision decision = this.authorizationManager.check(this::getAuthentication, request);
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthorizationEvent(this::getAuthentication, request, decision);
if (decision != null && !decision.isGranted()) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("Access Denied");
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
finally {
request.removeAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName);
}
}
private Authentication getAuthentication() {
Authentication authentication = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authentication == null) {
throw new AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException(
"An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext");
}
return authentication;
}
AuthorizationFilter에서 발생된 에러는 윗 단계인 ExceptionTranslationFilter에서 처리된다.
ExceptionTranslationHandler
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) {
handleAuthenticationException(request, response, chain, (AuthenticationException) exception);
}
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) {
handleAccessDeniedException(request, response, chain, (AccessDeniedException) exception);
}
}
private void handleAuthenticationException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain, AuthenticationException exception) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.logger.trace("Sending to authentication entry point since authentication failed", exception);
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain, exception);
}
private void handleAccessDeniedException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain, AccessDeniedException exception) throws ServletException, IOException {
Authentication authentication = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext().getAuthentication();
boolean isAnonymous = this.authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication);
if (isAnonymous || this.authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Sending %s to authentication entry point since access is denied",
authentication), exception);
}
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
this.messages.getMessage("ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
LogMessage.format("Sending %s to access denied handler since access is denied", authentication),
exception);
}
this.accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response, exception);
}
}
각각의 경로에 대해 권한을 다르게 설정할 수 있기 때문에, Authorization 과정에서 경로에 개별적으로 설정된 권한이 있는지 여부를 결정하여 권한이 설정이 되어 있는 경우 그에 해당하는 AuthorityManager을 호출하여 인가 검증을 수행한다.
Security Config
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
//인증 여부 처리
httpSecurity
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.requestMatchers("/user").hasRole("USER")
.requestMatchers("/admin").hasRole("ADMIN")
.requestMatchers("/sys").hasRole("SYS")
.anyRequest().permitAll();
httpSecurity.formLogin();
httpSecurity.rememberMe();
return httpSecurity.build();
}
위와 같이 보안 설정을 하면 아래에 총 4개의 경로에 대한 접근 권한 처리를 담당하는 AuthorityManager가 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
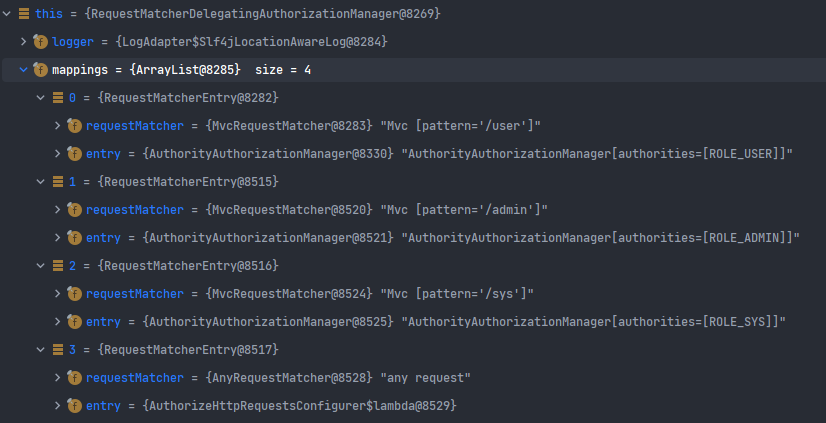
Authorization Flow
- AuthorityFilter은 우선 AuthorityAuthorizationManager을 호출해서 해당 유저에 대한 접근 권한 검증을 수행한다.
try {
AuthorizationDecision decision = this.authorizationManager.check(this::getAuthentication, request);
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthorizationEvent(this::getAuthentication, request, decision);
if (decision != null && !decision.isGranted()) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("Access Denied");
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
- AuthorityAuthorizationManager의 구현체인 RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager이 실행되면서, 특정 경로에 대한 접근이 권한이 설정되어 있는지 확인한다.
RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager
@Override
public AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, HttpServletRequest request) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authorizing %s", request));
}
for (RequestMatcherEntry<AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext>> mapping : this.mappings) {
RequestMatcher matcher = mapping.getRequestMatcher();
MatchResult matchResult = matcher.matcher(request);
if (matchResult.isMatch()) {
AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> manager = mapping.getEntry();
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Checking authorization on %s using %s", request, manager));
}
return manager.check(authentication,
new RequestAuthorizationContext(request, matchResult.getVariables()));
}
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.of(() -> "Denying request since did not find matching RequestMatcher"));
}
return DENY;
}
- 이후 RequestMatcherDelegatingAuthorizationManager의 상위 클래스인 AuthorityAuthorizationManager을 처리해서 접근 권한 검증을 수행한다.
AuthorityAuthorizationManager
@Override
public AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, T object) {
boolean granted = isGranted(authentication.get());
return new AuthorityAuthorizationDecision(granted, this.authorities);
}
private boolean isGranted(Authentication authentication) {
return authentication != null && authentication.isAuthenticated() && isAuthorized(authentication);
}
private boolean isAuthorized(Authentication authentication) {
Set<String> authorities = AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(this.authorities);
for (GrantedAuthority grantedAuthority : getGrantedAuthorities(authentication)) {
if (authorities.contains(grantedAuthority.getAuthority())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
References
link: inflearn
docs: spring_security

댓글남기기