Spring Security Part 1
Login Authentication
Initial Setting
build.gradle
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security'
build.gradle 파일에 위의 dependency를 적용하게 되면 spring security가 동작하게 되면서 모든 요청에 대해 로그인을 요구한다.
Spring Security Config
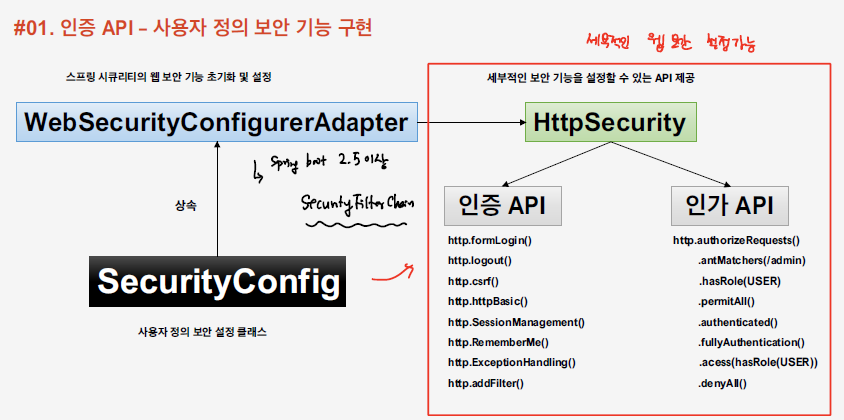
Spring Security의 경우 위와 같은 방식으로 인증, 인가를 처리하게 된다. Security Config을 정의하게 되면 이를 통해 HttpSecurity를 활용한 각종 인증,인가 로직을 설정할 수 있다.
Spring 2.5.7 이후로 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter는 deprecated 처리가 되었기 때문에 아래와 같이 SecurityFilterChain 클래스를 Bean으로 등록해서 각종 security 관련 설정을 진행하면 된다.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception{
//인증 여부 처리
httpSecurity
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
//로그인 처리
httpSecurity
.formLogin();
httpSecurity.build();
}
}
Form Login
Security의 formLogin() 메소드를 활성하게 되면, form 기반의 로그인 인증이 진행된다. 아래와 같이 각종 로그인에 관련된 설정을 지정할 수 있다.
//로그인 설정
httpSecurity
.formLogin() //form 기반의 로그인 인증 활성화
.loginPage("/loginPage") //사용자 정의 로그인 페이지로 redirect
.defaultSuccessUrl("/home") //로그인 성공 후 redirect url
.failureUrl("/login") //로그인 실패 시 redirect url
.usernameParameter("userId") //form login의 username parameter
.passwordParameter("passwd") //form login의 password parameter
.loginProcessingUrl("/login_proc") //post 요청을 처리하는 url mapping
.successHandler(new AuthenticationSuccessHandler() { //로그인 성공 이후에 실행되는 핸들러
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("authentication: " + authentication.getName());
response.sendRedirect("/");
}
})
.failureHandler(new AuthenticationFailureHandler() { ////로그인 실패 이후에 실행되는 핸들러
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("exception.getMessage() = " + exception.getMessage());
response.sendRedirect("/");
}
})
.permitAll(); //로그인 페이지에 대한 접근은 인증을 요구하지 않는다.
Login Flow
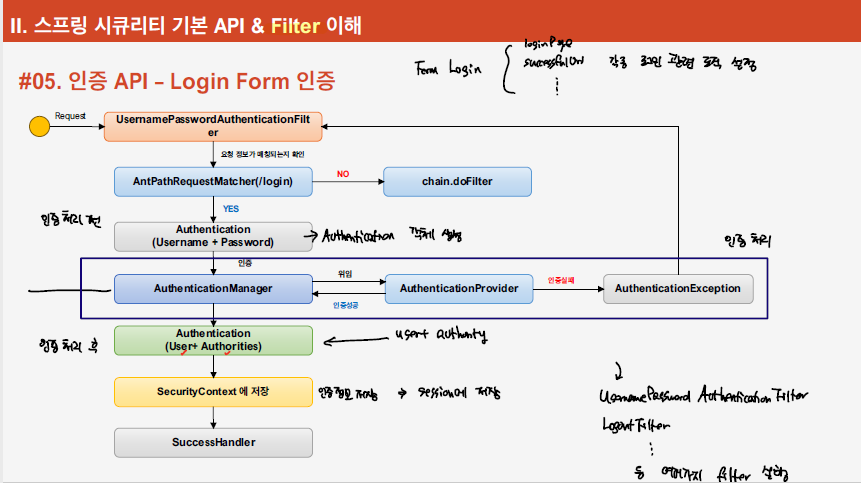
위의 흐름대로 spring security의 form login이 동작한다.
- 로그인 요청이 들어오면 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter가 요청을 받아서 로그인 처리를 진행하게 된다. 입력 받은 username, password 입력을 받아서 Authentication 객체를 만들어서 AuthencationManager에 Authentication 객체를 넘긴다.
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
username = (username != null) ? username.trim() : "";
String password = obtainPassword(request);
password = (password != null) ? password : "";
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username,
password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
- AuthenticationManager은 AuthenticationProvider로 인증을 위임하게 되면서, provider에서 인증을 수행한다.
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)",
provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size));
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
- AuthenticationProvider에서 username, password 기반으로 인증을 수행한다. 성공적으로 마무리 되면 Authentication 객체를 반환하게 된다.
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since no credentials provided");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) {
this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since password does not match stored value");
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages
.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials"));
}
}
- AuthenticationProvider에 의해 전달받은 Authentication 객체를 토대로 Security Context에 저장하게 되면서 해당 사용자에 대한 인증이 완료되었고 그 상태를 유지한다.
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContext context = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authResult);
this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setContext(context);
this.securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Set SecurityContextHolder to %s", authResult));
}
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(authResult, this.getClass()));
}
this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
Logout
로그아웃을 수행하게 되면, 기존의 저장된 세션을 비활성화면서, 인증토큰(Authentication), 쿠키, 등의 정보를 삭제한다.
//logout 설정
httpSecurity.logout() //로그아웃 기능 활성화
.logoutUrl("/logout") //로그아웃을 처리하는 url
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login") //로그아웃 이후, redirect url
.deleteCookies("JSESSIONID", "remember-me") //로그아웃 과정에서 삭제할 쿠키 정보
.addLogoutHandler(new LogoutHandler() { //로그아웃을 처리하는 핸들러
@Override
public void logout(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.invalidate();
}
})
.logoutSuccessHandler(new LogoutSuccessHandler() { //로그아웃 성공 시 실행되는 핸들러
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendRedirect("/login");
}
});
Logout Flow
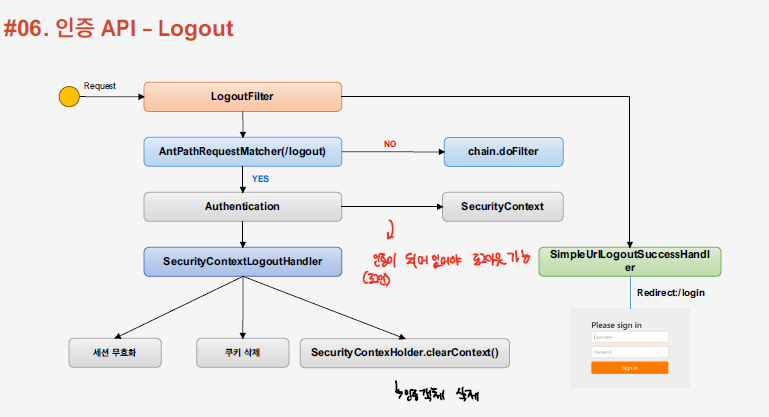
- Logout 요청이 들어오면 LogoutFilter가 동작하게 되고, 우선적으로 Security Context에 Authentication 객체가 있는지를 확인하여 인증이 완료된 상태인지 확인한다. 애초에 인증이 안되어있으면 로그아웃의 필요성이 없음
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (requiresLogout(request, response)) {
Authentication auth = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Logging out [%s]", auth));
}
this.handler.logout(request, response, auth);
this.logoutSuccessHandler.onLogoutSuccess(request, response, auth);
return;
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
- LogoutHandler을 구현하고 있는 SecurityContextLogoutHandler에 의해서 세션 무효화, 쿠키 삭제, security context 제거, 등의 작업을 수행한다.
@Override
public void logout(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) {
Assert.notNull(request, "HttpServletRequest required");
if (this.invalidateHttpSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
//세션 무효화
session.invalidate();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Invalidated session %s", session.getId()));
}
}
}
SecurityContext context = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext();
//security context 제거
this.securityContextHolderStrategy.clearContext();
if (this.clearAuthentication) {
context.setAuthentication(null);
}
}
//쿠키 제거
public CookieClearingLogoutHandler(String... cookiesToClear) {
Assert.notNull(cookiesToClear, "List of cookies cannot be null");
List<Function<HttpServletRequest, Cookie>> cookieList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String cookieName : cookiesToClear) {
cookieList.add((request) -> {
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(cookieName, null);
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
String cookiePath = StringUtils.hasText(contextPath) ? contextPath : "/";
cookie.setPath(cookiePath);
cookie.setMaxAge(0);
cookie.setSecure(request.isSecure());
return cookie;
});
}
this.cookiesToClear = cookieList;
}
Remember-Me
간혹, 사이트에서 로그인을 수행하는 과정에서 자동 로그인, 로그인 상태 유지, 등의 체크 박스를 둔 경우가 있는데, 이들 모두 세션이 만료되더라도 이후 재접속 시 로그인 상태를 유지하게끔 하여 자동으로 로그인되도록 하는 기능이다. 이러한 기능 제공을 위해 사이트에서 Remember-Me 쿠키를 발급해서 웹 브라우져에 저장한다.
//리멤버-미 처리(사용자의 로그인 기록 유지)
httpSecurity.rememberMe() //리멤버 비 기능 활성화
.rememberMeParameter("remember") //form 요청에서의 remember-me에 대한 설정값을 저장한 parameter
.tokenValiditySeconds(3600); //리멤버 쿠키의 만료기간 설정
아래를 보면, 로그인 성공 이후에 remember-me 쿠키가 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
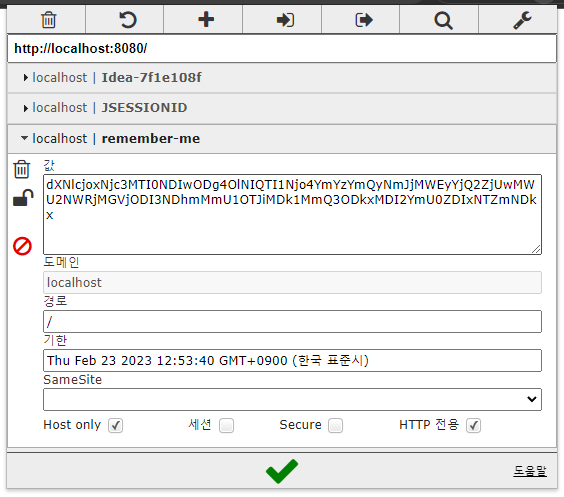
기존에는, JSESSION_ID 쿠키가 없는 상태로 접속을 하게 되면 로그인 창으로 redirect 되지만, 위와 같이 remember-me cookie가 있는 상태에서 JSESSION_ID를 제거한 상태로 접속을 하더라고 인증이 유지된 상태로 접속이 된다.
remember-me flow
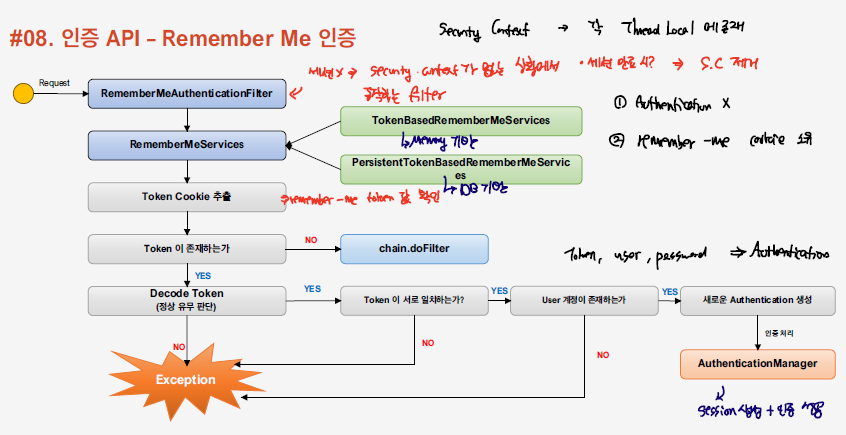
- RememberMeAuthenticationFilter은 요청에 대하여 Authentication 객체가 존재하는 지 여부와 Remember-me token이 존재하는 지 여부를 판단하여, remember-me 여부를 판단한다. remember-me token이 존재하게 되면 Authentication Manager로 인증을 위임한다.
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
//Authentication 객체 여부 확인
if (this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext().getAuthentication() != null) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage
.of(() -> "SecurityContextHolder not populated with remember-me token, as it already contained: '"
+ this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'"));
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
//Remember-me token 여부 확인
Authentication rememberMeAuth = this.rememberMeServices.autoLogin(request, response);
//Remember-me token이 있으면 remember-me 동작
if (rememberMeAuth != null) {
// Attempt authenticaton via AuthenticationManager
try {
rememberMeAuth = this.authenticationManager.authenticate(rememberMeAuth);
...
}
}
}
- AuthenticationManager을 통해 인증을 처리하고 SecurityContext에 Authentication 객체를 담는 과정을 진행한다.
// Store to SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContext context = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(rememberMeAuth);
this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setContext(context);
onSuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, rememberMeAuth);
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.of(() -> "SecurityContextHolder populated with remember-me token: '"
+ this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext().getAuthentication() + "'"));
this.securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response);
*. remember-me token을 만드는 과정, username, password, 만료일 기반으로 토큰을 생성해서, 로그인이 성공했을 때, 웹 브라우져에 쿠키를 저장하게 된다.
@Override
public void onLoginSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication successfulAuthentication) {
String username = retrieveUserName(successfulAuthentication);
String password = retrievePassword(successfulAuthentication);
// If unable to find a username and password, just abort as
// TokenBasedRememberMeServices is
// unable to construct a valid token in this case.
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(username)) {
this.logger.debug("Unable to retrieve username");
return;
}
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
UserDetails user = getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
password = user.getPassword();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(password)) {
this.logger.debug("Unable to obtain password for user: " + username);
return;
}
}
int tokenLifetime = calculateLoginLifetime(request, successfulAuthentication);
long expiryTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// SEC-949
expiryTime += 1000L * ((tokenLifetime < 0) ? TWO_WEEKS_S : tokenLifetime);
String signatureValue = makeTokenSignature(expiryTime, username, password, this.encodingAlgorithm);
setCookie(new String[] { username, Long.toString(expiryTime), this.encodingAlgorithm.name(), signatureValue },
tokenLifetime, request, response);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(
"Added remember-me cookie for user '" + username + "', expiry: '" + new Date(expiryTime) + "'");
}
}
Anonymous User
인증이 되지 않은 유저를 익명 사용자라고 하는데, Spring Security에서는 익명 사용자라는 개념을 두어서 인증 된 사용자와 그렇지 않은 사용자들을 구분하게 된다. Security Context에 Authentication 객체가 있는지 여부를 판단하는 것이 아닌, Authentication 내부 권한값을 활용하여 서로를 구분한다. 이는, 모든 유저는 Authentication 객체를 가지고 있는 통일된 상태에서 어플리케이션을 동작하도록 하기 위함이다. Java에서 Optional 객체를 활용하는 개념과 유사하다고 볼 수 있다.
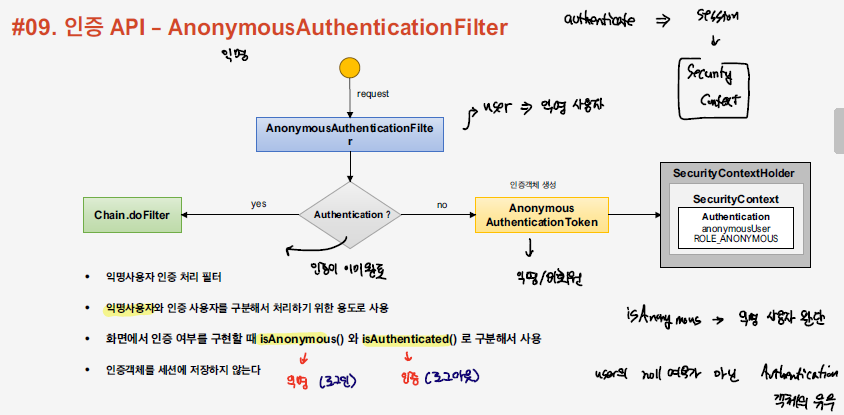
private SecurityContext defaultWithAnonymous(HttpServletRequest request, SecurityContext currentContext) {
Authentication currentAuthentication = currentContext.getAuthentication();
//Authentication 객체 존재하지 않으면
if (currentAuthentication == null) {
//익명 사용자 기반의 인증토큰을 생성한다.
Authentication anonymous = createAuthentication(request);
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.of(() -> "Set SecurityContextHolder to " + anonymous));
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Set SecurityContextHolder to anonymous SecurityContext");
}
SecurityContext anonymousContext = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext();
anonymousContext.setAuthentication(anonymous);
return anonymousContext;
}
else {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace(LogMessage.of(() -> "Did not set SecurityContextHolder since already authenticated "
+ currentAuthentication));
}
}
return currentContext;
}
//익명 사용자 토큰을 생성하는 메소드
protected Authentication createAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
AnonymousAuthenticationToken token = new AnonymousAuthenticationToken(this.key, this.principal,
this.authorities);
token.setDetails(this.authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request));
return token;
}
References
link: inflearn
docs: spring_security

댓글남기기