Java Spring MVC part 15
API Exception Handling
Spring이 제공하는 BasicErrorController을 이용하면 발생한 오류에 대해 오류 페이지를 띄우는 작업을 손쉽게 진행할 수 있다. 하지만, API 호출을 통한 오류 정보를 처리하는 과정에서는, JSON 형태로 데이터를 변환하는 작업이 요구된다.
Servelet
WebServerCustomizer
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableWebServerFactory factory) {
ErrorPage errorPage404 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "/error-page/404");
ErrorPage errorPage500 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, "/error-page/500");
ErrorPage errorPageEx = new ErrorPage(RuntimeException.class, "/error-page/500");
factory.addErrorPages(errorPage404, errorPage500, errorPageEx);
}
ApiExceptionController
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class ApiExceptionController {
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("ex")) {
throw new RuntimeException("잘못된 사용자");
}
return new MemberDto(id, "hello " + id);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class MemberDto {
private String memberId;
private String name;
}
}
위와 같은 controller을 구성했을 경우, 아래와 같은 결과를 보인다.
http://localhost:8080/api/members/spring
{
"memberId": "spring",
"name": "hello spring"
}
정상적인 요청에 대해서는 JSON 형태의 MemberDTO가 정상적으로 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
http://localhost:8080/api/members/ex
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" style="max-width: 600px">
<div class="py-5 text-center">
<h2>500 오류 화면</h2>
</div>
<div>
<p>오류 화면 입니다.</p>
</div>
<hr class="my-4">
</div> <!-- /container -->
</body>
</html>
하지만, 위와 같이 예외가 발생하는 부분에 대해서는, 예외처리 과정에 따라 오류 페이지 html이 전달되게 된다. 이는, 클라이언트 측에서 기대한 API 결과물이 아니다. html이 아닌 JSON 형태로 전달해야 된다.
ErrorPageController
@RequestMapping(value="/error-page/500",produces= MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String,Object>> errorPage500Api(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.info("API error page 500");
HashMap<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
Exception ex = (Exception) request.getAttribute(ERROR_EXCEPTION);
result.put("status", request.getAttribute(ERROR_STATUS_CODE));
result.put("message", ex.getMessage());
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE);
return new ResponseEntity<>(result, HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode));
}
위와 같이, @RequestMapping에 produces를 명시하게 되면, 생성되는 media-type를 지정할 수 있다. 즉, HttpRequest의 Accept에 전달되는 값에 따라 해당 메서드의 실행여부가 결정된다.
http://localhost:8080/api/members/ex
{
"message": "잘못된 사용자",
"status": 500
}
위의 ErrorController에 Exception Handler 부분에 JSON 객체를 반환하도록 설정하였고, 실제로 위와 같이 JSON 객체를 반환하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
BasicErrorController
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response) {}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {}
BasicErrorController는 위와 같이 설계되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있어, request의 accept 헤더값이 text/html 인 경우, errorHtml()을 호출하게 되고, 나머지의 경우 JSON 형태로 반환하는 error()를 출력하게 된다.
따라서, 위의 경우에도 Spring에서 기본적으로 JSON 형태로 오류 정보로 반환하도록 한다.
http://localhost:8080/api/members/ex
{
"timestamp": "2021-04-28T00:00:00.000+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"exception": "java.lang.RuntimeException",
"trace": "java.lang.RuntimeException: 잘못된 사용자\n\tat
hello.exception.web.api.ApiExceptionController.getMember(ApiExceptionController
.java:19...",
"message": "잘못된 사용자",
"path": "/api/members/ex"
}
또한, exception, message, trace와 같은 오류와 관련된 정보는 application.properties의 설정에 따라 포함하도록 할 수 있고, 생략할 수 있는데, 오류정보는 최대한 노출하지 않는 것이 보안상에 좋다.
BasicErrorController을 이용해서 오류 코드에 맞는 Html 오류 페이지를 출력하는 것은 용이하다. 하지만, API의 경우, 각 컨트롤러나 예외에 마다 서로 다른 응답 결과를 출력해야하는 경우가 존재한다. BasicErrorController을 확장해서 서로 다른 API 오류를 처리하도록 할 수 있지만, 보통의 경우 @ExceptionHandler를 통해서 처리한다. 우선은, 예외를 처리하는 ExceptionResolver에 대해 알아보자
HandlerExceptionResolver
서버 내부에서 발생되는 오류에 대해서 서버에서는 500(Internal Server Error)로 처리하게 된다. 하지만, 때에서 따라서 400,404와 같은 에러로 변환해서 처리해야 될 때가 존재한다.
Error Controller
@GetMapping("/api/members/{id}")
public MemberDto getMember(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
if (id.equals("bad")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("잘못된 입력 값");
}
}
Response
{
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"exception": "java.lang.IllegalArgumentException",
"path": "/api/members/bad"
}
Spring에서는 컨트롤러 밖으로 전달된 예외를 잡아서 처리할 수 있는 방법을 제공하는데, 이것이 HandlerExceptionResolver라는 것이다. 아래의 그림을 통해 동작과정을 살펴보자
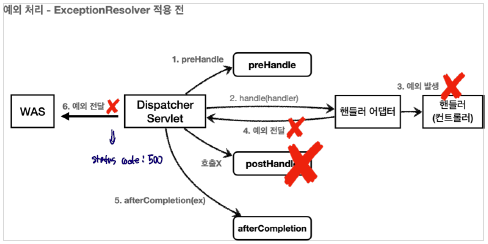
ExceptionResolver을 사용하기 전에는 예외가 WAS로 전달되어서 처리된다.
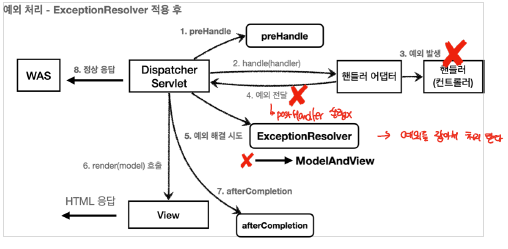
하지만, ExceptionResolver을 사용하게 되면 컨트롤러에서 발생한 예외를 잡아서 오류를 처리한 이후에는 정상적인 흐름으로 인식하게 된다.
HandlerExceptionResolver Interface
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
ModelAndView resolveException(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex);
}
ExceptionResolver는 인터페이스 형태로 제공되며, 위의 resolveException 메소드를 구현해서 resolver로 등록하게 되면 해당 ExceptionResolver가 예외 처리과정에서 작동하게 된다.
Resolver Register
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
resolvers.add();
}
}
MyHandlerExceptionResolver
@Slf4j
public class MyHandlerExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
try {
if (ex instanceof IllegalArgumentException) {
log.info("IllegalArgumentException resolver to 400");
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, ex.getMessage());
return new ModelAndView();
}
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
위의 exception resolver의 경우 IllegalArgumentException에 대한 처리를 수행한다. response.sendError()를 이용해서 새로운 상태코드로 지정하게 되고, 마지막에 ModelAndView를 호출해서 정상적인 흐름처럼 이어지도록한다.
HandlerExceptionResolver을 이용해서 다양한 방식으로 에러를 처리하는 것이 가능하다.
- 빈 ModelAndView를 반환하는 경우: 뷰 랜더링을 수행하지 않는다.
- ModelAndView에 특정 view 경로 지정: 새로운 오류 화면을 출력하도록 할 수 있다.
- Null: 다음 ExceptionResolver을 호출하게 되고, 만약에 계속해서 처리되지 않고 넘어가면 결국에는 WAS로 예외가 전달된다.
위와 같이 ExceptionResolver을 이용하게 되면 WAS까지 예외가 넘어가지 않고, 중간에 처리를 하기 때문에 오류 처리 과정을 간략화 할 수 있는 장점이 있다.
JSON 형태의 오류 정보를 출력하는 ErrorResolver
if (ex instanceof UserException) {
log.info("UserException resolver to 400");
String accept = request.getHeader("accept");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST);
if (accept.equals("application/json")) {
log.info("handling UserException");
Map<String, Object> errorResult = new HashMap<>();
errorResult.put("ex", ex.getClass());
errorResult.put("message", ex.getMessage());
String result = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(errorResult);
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(result);
return new ModelAndView();
}
else{
return new ModelAndView("error/500");
}
}
위와 같이 직접 response를 구성해서 API를 출력하도록 할 수 있다.
Spring Based ExceptionResolver
ExceptionResolver을 직접 구현해서 사용하게 되면 매우 복잡한 것을 확인할 수 있다. 그래서, Spring에서는 자동으로 이러한 ExceptionResolver에 대해서 구현해놓았다.
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
- ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
- DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
Spring에서는 위의 순서대로 ExceptionResolver가 실행된다.
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
@ResponseStatus을 포함하는 예외, ResponseStatusException 예외에 대한 처리를 수행한다.
@ResponseStatus
@GetMapping("/api/response-status-ex1")
public String responseStatusEx1(){
throw new BadRequestException();
}
@ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST, reason = "잘못된 요청 오류")
public class BadRequestException extends RuntimeException {
}
위와 같이 @ResponseStatus가 붙어있는 예외에 대해서 Resolver가 동작하게되며, code를 이용해서 설정하고자하는 HttpStatus를 지정할 수 있고, reason에는 오류메세지를 지정할 수 있다. reason 속성에 message 코드를 지정하여, messaging도 활용할 수 있다.
http://localhost:8080/api/response-status-ex1?message=
{
"status": 400,
"error": "Bad Request",
"exception": "hello.exception.exception.BadRequestException",
"message": "잘못된 요청 오류",
"path": "/api/response-status-ex1"
}
ResponseStatusException
@ResponseStatus는 개발자가 직접 예외에 대한 조작을 수행할 수 있는 경우, 활용할 수 있는 방안이다. 하지만, 직접 annotation을 추가할 수 없는 경우, ResponseStatusException을 활용하는 방법이 있다.
ErrorController
@GetMapping("/api/response-status-ex2")
public String responseStatusEx2(){
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "error.bad", new IllegalArgumentException());
}
http://localhost:8080/api/response-status-ex2
{
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"exception": "org.springframework.web.server.ResponseStatusException",
"message": "잘못된 요청 오류입니다. 메시지 사용",
"path": "/api/response-status-ex2"
}
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
스프링 내부에서 발생되는 오류에 대한 처리를 수행한다. 대표적으로 Parameter Binding이 잘못되는 경우 발생되는 TypeMismatchException에 대한 처리를 수행한다. 보통은 Server 내부의 오류에 대해서는 오류코드가 500으로 설정되는데, 위의 경우 400 오류로 변환된다.
ErrorController
@GetMapping("/api/default-handler-ex")
public String defaultException(@RequestParam Integer data){
return "ok";
}
위와 같이 Integer을 받는 parameter에 문자 형태의 입력이 들어오면 TypeMistmatchException이 발생하는데, 이때 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver가 동작하게 된다.
http://localhost:8080/api/default-handler-ex?data=hello&message=
{
"status": 400,
"error": "Bad Request",
"exception":
"org.springframework.web.method.annotation.MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException"
,
"message": "Failed to convert value of type 'java.lang.String' to required
type 'java.lang.Integer'; nested exception is java.lang.NumberFormatException:
For input string: \"hello\"",
"path": "/api/default-handler-ex"
}
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
기존에 ExceptionResolver의 경우, 직접 구현해서 사용하는 과정이 상당히 복잡했다. 또한, 매번 ModelAndView을 반환하도록 되어 있고, JSON 형태로 출력하고자 하는 경우, response 객체에 직접 응답을 추가해야했다. 이러한 과정은 API 오류를 처리하기 복잡하게 만드는데, 이러한 API 오류를 손쉽게 처리하도록 하는 방법이 @ExceptionHandler을 이용하는 것이다.
Error Result
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ErrorResult {
private String code;
private String message;
}
API로 전달한 Error 객체를 지정한다.
@ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHandle(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
위와 같이, @ExceptionHandler에 처리하고자 하는 exception 정보를 설정한 다음오류 발생시 수행하고자 하는 메소드를 등록할 수 있다.
{
"code": "BAD",
"message": "잘못된 입력 값"
}
@ExceptionHandler에 오류 클래스를 지정하면 해당 클래스 뿐만아니라, 클래스를 상속하고 있는 자식클래스까지 처리하게 된다.
또한 @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)을 추가해서, 해당 오류에 대해서 상태코드를 변환해서 전달하도록 설정할 수 있다.
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class) //IllegalArgumentException 처리
public ErrorResult illegalExHandle(IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("BAD", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler //이렇게 exceptionHandler에 아무런 인자를 전달하지 않는 경우, 메소드에 전달되는 오류 클래스 인자를 보고, 해당 오류에 대한 처리를 수행한다.
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandle(UserException e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler //이 메소드의 경우 모든 오류 클래스의 부모 클래스인 Exception 클래스를 처리하므로, 위에서 처리하지 못한 에러대해서는 해당 메소드로 처리되게 된다.
public ErrorResult exHandle(Exception e) {
log.error("[exceptionHandle] ex", e);
return
}
@ExceptionHandler(ViewException.class) //ModelAndView를 반환해서 원하는 오류화면이 출력되도록 지정할 수 있다.
public ModelAndView ex(ViewException e) {
log.info("exception e", e);
return new ModelAndView("error");
}
@ControllerAdvice
기본적으로 @ExceptionHandler로 지정한 예외처리는 해당 @ExceptionHandler가 위치한 컨트롤러 클래스에 대한 예외만 처리하게 된다. 하지만 @ControllerAdvice를 이용하게 되면 모든 컨트롤러에 대해 글로벌하게 사용될 수 있도록 지정할 수 있다.
RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExControllerAdvice {
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalArgumentException.class)
public ErrorResult illegalExHandler(IllegalArgumentException e){
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("Bad", e.getMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResult> userExHandler(UserException e){
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
ErrorResult errorResult = new ErrorResult("USER-EX", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity(errorResult, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
@ExceptionHandler
public ErrorResult exHandler(Exception e){
log.error("[exceptionHandler] ex", e);
return new ErrorResult("EX", "내부 오류");
}
}
@RestControllerAdvice는 @RestController에 대한 ControllerAdvice로 @ResponseBody를 포함하고 있어, JSON 형태의 오류정보를 출력하는 경우에 활용된다.
대상 클래스 지정
//RestController annotation이 등록된 컨트롤러에 대해서만 ExceptionHandler 수행
@ControllerAdvice(annotations = RestController.class)
public class ExampleAdvice1 {}
//특정 패키지 내에 속한 controller에 대해서만 ExceptionHandler 수행
@ControllerAdvice("org.example.controllers")
public class ExampleAdvice2 {}
//특정 클래스에 대해서만 ExceptionHandler 수행
@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = {ControllerInterface.class,
AbstractController.class})
public class ExampleAdvice3 {}
보통, @ExceptionHandler 와 @ControllerAdvice를 이용해서 대부분의 예외를 처리할 수 있다.
References
link: inflearn
link:springmvc

댓글남기기