Java Spring Advanced part 11
Limitations
Spring AOP 방식을 통한 프록시 방식을 취하면서 발생하는 문제점들이 존재한다.
Internal Calls
보통은 AOP를 적용하기 위해서는, proxy를 통한 target를 호출해야한다. 하지만, target 내부에서 target의 다른 메소드를 호출하는 경우 AOP가 적용되지 않는다.
Service
public class CallServiceV0 {
public void external() {
log.info("call external");
internal();
}
public void internal() {
log.info("call internal");
}
}
AOP
public class CallLogAspect {
@Before("execution(* hello.aop.internalcall..*.* (..))")
public void doLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("aop= {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
}
}
위와 같이, Service와 Aop를 구성하고 아래에 대해서 테스트를 수행한다.
Test
class CallServiceV0Test {
@Autowired
CallServiceV0 callService;
@Test
void external() {
callService.external();
}
원래, 위의 포인트컷의 의도에 따르면 hello.aop.internallcall내의 모든 메소드에 대해서 AOP를 적용하는 것이다. 하지만 실제로 위의 테스트를 수행해보면 아래의 결과와 같이, internal 메소드에 대해서는 AOP가 적용되지 않는다.
Results
CallLogAspect : aop=void hello.aop.internalcall.CallServiceV0.external()
CallServiceV0 : call external
CallServiceV0 : call internal
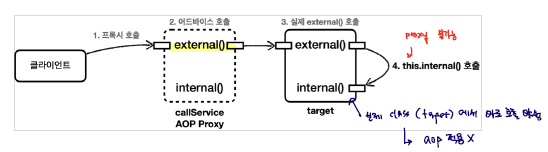
이는, 프록시를 거쳐서 실행해야 advice를 실행시킬 수 있는데, 그렇지 못하고 internal 메소드를 호출 할때 target 객체에서 internal 메소드를 호출하기 때문에 그런것이다.
위와 같이 내부 호출을 하는 경우에 대해서는, advice가 적용되지 않는다. 위와 같은 문제는 프록시 방식을 취하는 Spring AOP에서 발생하는 문제이다. AspectJ를 직접적으로 활용하면 실제 advice 코드가 추가되어 이런 문제가 발생하지 않지만, 러닝 타임 위빙, JVM 옵션의 설정 등의 복잡한 문제가 있어 Aspect 방식은 잘 활용하지 않는다.
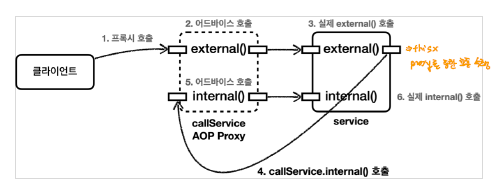
Solution 1 - Self DI
프록시를 통해서 호출하면 advice를 활용할 수 있기 때문에, 프록시 객체를 주입하면 Advice가 실행된다.
Service
@Slf4j
@Component
public class CallServiceV1 {
private CallServiceV1 callService;
// @Autowired
public void setCallService(CallServiceV1 callService) {
this.callService = callService;
}
public void external() {
log.info("call external");
callService.internal();
}
public void internal() {
log.info("call internal");
}
}
대신, 순환 참조가 발생할 수 있으므로 위와 같이 수정자 방식의 DI를 취해줘야한다.
Results
CallLogAspect : aop=void hello.aop.internalcall.CallServiceV1.external()
CallServiceV2 : call external
CallLogAspect : aop=void hello.aop.internalcall.CallServiceV1.internal()
CallServiceV2 : call internal
internall 메소드에 대해서도 정상적으로 수행되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Solution 2 - Lazy Loading
위의 방식과 유사한데, 대신 생성자 주입 방식을 활용한다. 이때, 객체가 아직 생성되기 전이므로 ObjectProvider을 통한 지연 조회 방식을 통해 객체를 나중에 주입받도록 한다.
Service
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CallServiceV2 {
@Autowired
private final ObjectProvider<CallServiceV2> callServiceProvider;
public void external() {
log.info("call external");
CallServiceV2 callService = callServiceProvider.getObject();
callService.internal();
}
public void internal() {
log.info("call internal");
}
}
Results
CallLogAspect : aop=void hello.aop.internalcall.CallServiceV2.external()
CallServiceV2 : call external
CallLogAspect : aop=void hello.aop.internalcall.CallServiceV2.internal()
CallServiceV2 : call internal
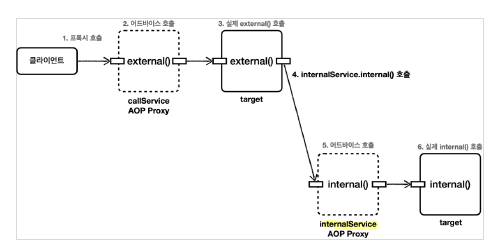
Solution 3 - Structure Change
가장 좋은 방법은 내부 호출을 하지 않도록 코드를 설계하는 것이다.
Service
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CallServiceV3 {
private final InternalService internalService;
public void external() {
log.info("call external");
internalService.internal();
}
}
@Slf4j
@Component
public class InternalService {
public void internal() {
log.info("call internal");
}
}
Results
CallLogAspect : aop=void hello.aop.internalcall.CallServiceV3.external()
CallServiceV3 : call external
CallLogAspect : aop=void hello.aop.internalcall.InternalService.internal()
InternalService : call internal
보통의 AOP의 경우 public 메소드에 대해서만 로그 출력을 하도록 설정한다. private의 경우는 AOP를 적용하지 않는다. 따라서, 큰 기능을 담당하는 메소드의 경우 내부 호출을 사용하지 않고, 따로 class로 분리해서 생각해야한다.
Type Casting
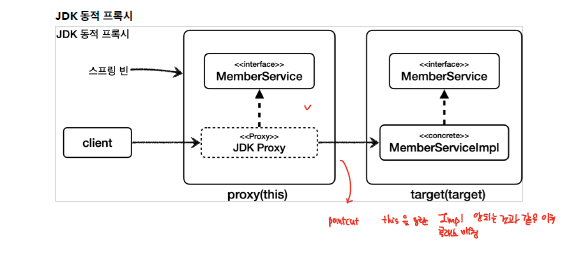
구현 클래스만 있는 경우에는 CGLIB 방식을 취해야하지만, 인터페이스가 있는 경우에는 JDK 프로시 혹은 CGLIB 방식을 둘 중 하나를 선택할 수 있다.
JDK Proxy 방식을 활용해서 프록시를 구성하게 되면, 구현 클래스에 대한 타입 캐스팅이 불가능하다.
JDK proxy type casting
void jdkProxy() {
MemberServiceImpl target = new MemberServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(false); // JDK proxy
// Proxy -> MemberService Casting
MemberService memberServiceProxy = (MemberService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("proxy={}", memberServiceProxy.getClass());
//Proxy -> MemberServiceImpl Casting
Assertions.assertThatThrownBy(()->
{
MemberServiceImpl memberServiceImplProxy = (MemberServiceImpl) proxyFactory.getProxy();
})
.isInstanceOf(ClassCastException.class);
}
위의 Test를 보면 알듯이, JDK 프록시 방식을 활용하는 경우 구현 클래스에 대한 type casting 수행시, ClassCastException 예외가 발생되는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이는 JDK 프록시 방식이 아래의 그림을 보면 알듯이, Interface를 참조해서 프록시를 만들기 때문에, 구현 클래스에 대한 정보를 확인할 수 없다. 즉, JDK 프로시는 구현 클래스와 아무 연관성이 없다.
CGLIB type casting
@Test
void cglibProxy() {
MemberServiceImpl target = new MemberServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); // CGLIB proxy
// Proxy -> MemberService Casting
MemberService memberServiceProxy = (MemberService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("MemberService proxy={}", memberServiceProxy.getClass());
//Proxy -> MemberServiceImpl Casting
MemberService memberServiceImplProxy = (MemberServiceImpl) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("MemberServiceImpl proxy={}", memberServiceImplProxy.getClass());
}
Results
22:09:00.752 [main] INFO hello.aop.proxyvs.ProxyCastingTest - MemberService proxy=class hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$8918cd22
22:09:00.755 [main] INFO hello.aop.proxyvs.ProxyCastingTest - MemberServiceImpl proxy=class hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$8918cd22
CGLIB의 경우 구현 클래스 기반으로 프록시를 생성하기 때문에, 구현 클래스로의 type casting이 가능하다.
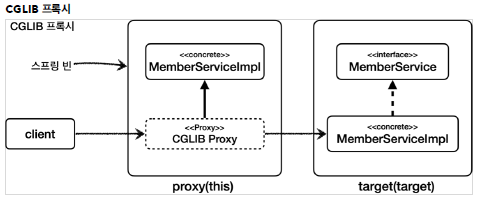
DI Problems
JDK 프로시 방식을 취하면, 구현 클래스에 대한 DI가 불가능하다.
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false"})
@SpringBootTest
@Import(ProxyDIAspect.class)
public class ProxyDITest {
@Autowired
MemberService memberService;
@Autowired
MemberServiceImpl memberServiceImpl;
@Test
public void go() {
log.info("MemberSerice={}", memberService.getClass());
log.info("MemberServiceImpl={}", memberServiceImpl.getClass());
memberService.hello("hello");
}
}
아래의 proxy-target-class를 false로 하면 JDK 프록시 방식을 취한다.
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false"})
Results
Bean named 'memberServiceImpl' is expected to be of type 'hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl' but was actually of type 'com.sun.proxy.$Proxy52'
TypeCasting 문제와 동일한 원인이다. 하위 클래스에 상위 클래스를 이용해서 초기화하려고 해서 발생하는 문제이다.
CGLIB 방식을 이용하면 정상적으로 DI를 받아서 구현 클래스를 사용하는 것이 가능하다.
아래의 proxy-target-class를 false로 하면 JDK 프록시 방식을 취한다.
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true"})
Results
2022-09-18 22:14:58.465 INFO 25384 --- [ main] hello.aop.proxyvs.ProxyDITest : MemberSerice=class hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$f602ce5c
2022-09-18 22:14:58.466 INFO 25384 --- [ main] hello.aop.proxyvs.ProxyDITest : MemberServiceImpl=class hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$f602ce5c
2022-09-18 22:14:58.469 INFO 25384 --- [ main] hello.aop.proxyvs.code.ProxyDIAspect : [LogDIAspect] String hello.aop.member.MemberServiceImpl.hello(String)
CGLIB Problems
클래스 기반으로 프록시를 만들기 때문에, 아래와 같이 상속으로 인한 문제점이 발생한다.
- target 클래스에 대한 기본 생성자(non_args_constructor)가 필수적으로 요구된다.
- target 클래스를 부모 클래스로 해서 프록시가 자식 클래스가 되는 구조이다. 따라서, 자식 클래스에서는 필수적으로 부모 클래스의 생성자를 호출해야하는데, 이때 자동적으로 super()을 호출하기 때문에, target class(부모 클래스)에 대해서는 기본 생성자가 필요하다.
- 생성자가 2번 호출되는 문제점 발생
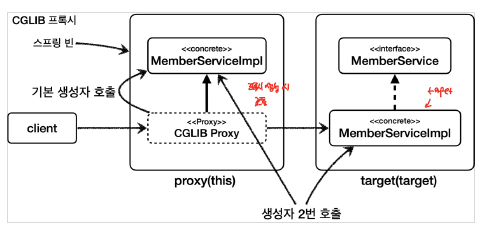
- 프록시 클래스를 만들때와, target 클래스를 만들 때, 총 2번에 걸쳐서 부모 클래스의 생성자가 호출된다.
- final class, method 사용 불가능
- final class로 설정하게 되면 상속을 받는 것이 불가능하고, final 메소드를 설정하게 되면 해당 메소드는 오버라이딩이 불가능하다.
Spring AOP solutions
Spring에서는 버전 업데이트를 통해 CGLIB가 가지는 문제점들을 해결하였다. 따라서 프록시를 취할때는 기본적으로 CGLIB 방식을 취한다.
References
link: inflearn
link:spring_advanced

댓글남기기