[Programmers] P67259 경주로 건설
[Programmers] P67259 경주로 건설
Question
Language: Python
Solution
해당 문제는 bfs를 수행하면서 각각의 목적지까지의 도달 과정에 있어 최소 비용을 구하는 문제이다. 그러므로, 각각의 경로에 대해 거리를 저장하는 배열(dp)가 필요하다. 각각의 좌표를 지나면서 발생한 비용과 해당 좌표에 저장된 최소 비용과 비교를 하면서 이동 여부를 결정한다.
if next_cost<=price[next_row][next_col]:
price[next_row][next_col]=next_cost
queue.append((next_row,next_col,next_dir,next_cost))
주의
아래와 같이 비용만 저장하게 되면 방향에 따른 비용 변화가 발생할 수 있기 때문에, 변화를 변수로 추가로 고려해줘야한다.
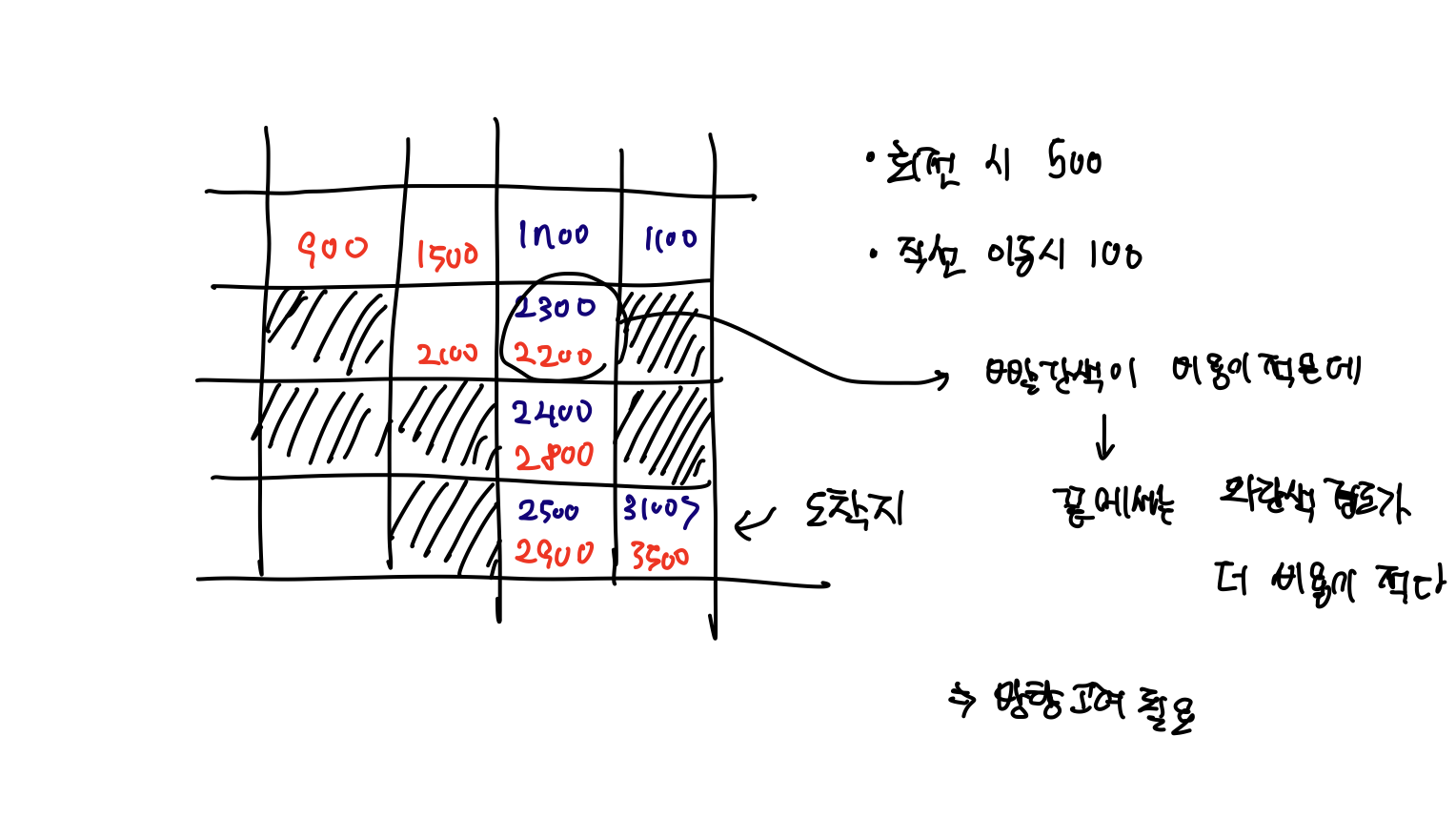
#price[방향][x좌표][y좌표]
price=[[[inf] * length for _ in range(length)] for in range(4)]
이러한 경로가 2개가 발생하는 이유는 시작점에서 오른쪽 길과 아래쪽 길을 선택할 수 있기 때문인데, 이를 위해 bfs을 2번 수행하는 것도 방법이 될 수 있다.
Solution 1
3차원 dp를 활용하는 방식(방향을 추가 고려) 개인적으로는 3차원 dp를 이용하는 방식 추후, dynamic programming 문제 풀이에 도움이 될것으로 생각된다.
from math import inf
from collections import deque
def solution(board):
answer = 0
min_result=inf
length=len(board)
dy=[-1,0,1,0]
dx=[0,1,0,-1]
price=[[[inf] * length for _ in range(length)] for _ in range(4)]
price[1][0][0]=0
price[2][0][0]=0
#row,col,dir,distance,direction_change
queue=deque([])
queue.append((0,0,1,0))
queue.append((0,0,2,0))
while queue:
row,col,direction,cost=queue.popleft()
if row==length-1 and col==length-1:
continue
for i in range(4):
next_dir=(direction+i)%4
next_row=row+dy[next_dir]
next_col=col+dx[next_dir]
next_cost=0
if next_row < 0 or next_row >=length or next_col < 0 or next_col>=length:
continue
if board[next_row][next_col] ==1:
continue
if i==0:
next_cost=cost+100
else:
next_cost=cost+600
if next_cost<=price[next_dir][next_row][next_col]:
price[next_dir][next_row][next_col]=next_cost
queue.append((next_row,next_col,next_dir,next_cost))
answer=min(price[0][-1][-1],price[1][-1][-1],price[2][-1][-1],price[3][-1][-1])
return answer
Solution 2
bfs를 2번 순회하는 방식
from math import inf
from collections import deque
def bfs(board,dir):
dy=[-1,0,1,0]
dx=[0,1,0,-1]
length=len(board)
price=[[inf] * length for _ in range(length)]
#row,col,dir,cost
queue=deque([])
queue.append((0,0,dir,0))
while queue:
row,col,direction,cost=queue.popleft()
if row==length-1 and col==length-1:
continue
for i in range(4):
next_dir=(direction+i)%4
next_row=row+dy[next_dir]
next_col=col+dx[next_dir]
next_cost=0
if next_row < 0 or next_row >=length or next_col < 0 or next_col>=length:
continue
if board[next_row][next_col] ==1:
continue
if i==0:
next_cost=cost+100
else:
next_cost=cost+600
if next_cost<=price[next_row][next_col]:
price[next_row][next_col]=next_cost
queue.append((next_row,next_col,next_dir,next_cost))
return price[-1][-1]
def solution(board):
answer = 0
min_result=inf
answer=min(bfs(board,1),bfs(board,2))
return answer

댓글남기기