[BOJ] Q2517 달리기
[BOJ] Q2517 달리기
Question
Language: Python
Difficulty: Platinum 4
해당 문제는 segment tree를 활용하여 풀이가 가능한 문제이다.
현재 인덱스보다 앞에 있는 값들에 대해서, 현재 값보다 작은 값들은 제칠 수 있기 때문에, 본인 인덱스를 기준으로 작은 값들의 갯수를 구해야한다.
우선적으로, (index, value)으로 이루어진 배열에 대해서, value를 기준으로 정렬을 진행한다.
그러면, value를 순차적으로 활용하기 때문에 현재 인덱스 보다 앞에 있는 숫자가 있다면, 이는 value보다 작은 값이 이기 때문에 그 만큼 순위를 높일 수 있게 된다.
만약 현재 index가 5라고 했을 때, index[1]+index[2]+index[3]+index[4]을 한 값이 본인보다 작은 수의 갯수가 되는 것이다. 이런식으로 반복을 진행하게 되면, 특정 구간에 대한 구간합을 요하는 문제가 되기 때문에 segment tree를 이용하여 문제 풀이가 가능하다.
각 index에 저장된 값은 해당 index에 대한 숫자가 있는지 여부를 의미하게 된다.
segment tree 활용
#1~index-1 까지의 구간합을 구하기 위한 함수 호출
count=query(segment_tree,1,1,n,1,index-1)
#index에 1을 추가함으로써 해당 index에 값이 있음을 나타냄
rankings[index-1]=(index-count)
update(segment_tree,1,1,n,index)
Solution 1
def query(trees,index,start,end,left,right):
if right < start or end < left:
return 0
if left <= start and end <=right:
return trees[index]
mid=(start+end)//2
return query(trees,index*2,start,mid,left,right) + query(trees,index*2+1,mid+1,end,left,right)
def update(trees,index,start,end,changed_index):
if changed_index < start or end < changed_index:
return
trees[index]+=1
if start==end:
return
mid=(start+end)//2
update(trees,index*2,start,mid,changed_index)
update(trees,index*2+1,mid+1,end,changed_index)
def solution():
segment_tree=[0]*(4*n)
numbers.sort()
rankings=[0]*n
for number,index in numbers:
count=query(segment_tree,1,1,n,1,index-1)
rankings[index-1]=(index-count)
update(segment_tree,1,1,n,index)
for ranking in rankings:
print(ranking)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n=int(input())
numbers=[(int(input()),i+1) for i in range(n)]
solution()
Solution 2
혹은 이 문제는 inversion counting algorithm을 응용해서 풀이하는 것이 가능하다. inversion counting 이란 i<j 에 대하여 a[i]>a[j]을 만족하는 경우에 inversion이 발생함을 의미한다. 즉 자기 보다 뒤에 있는 값이 자기 보다 작은 경우에 발생할 수 있다. 이때 이 inversion의 갯수를 구하는 것이다.
inversion counting
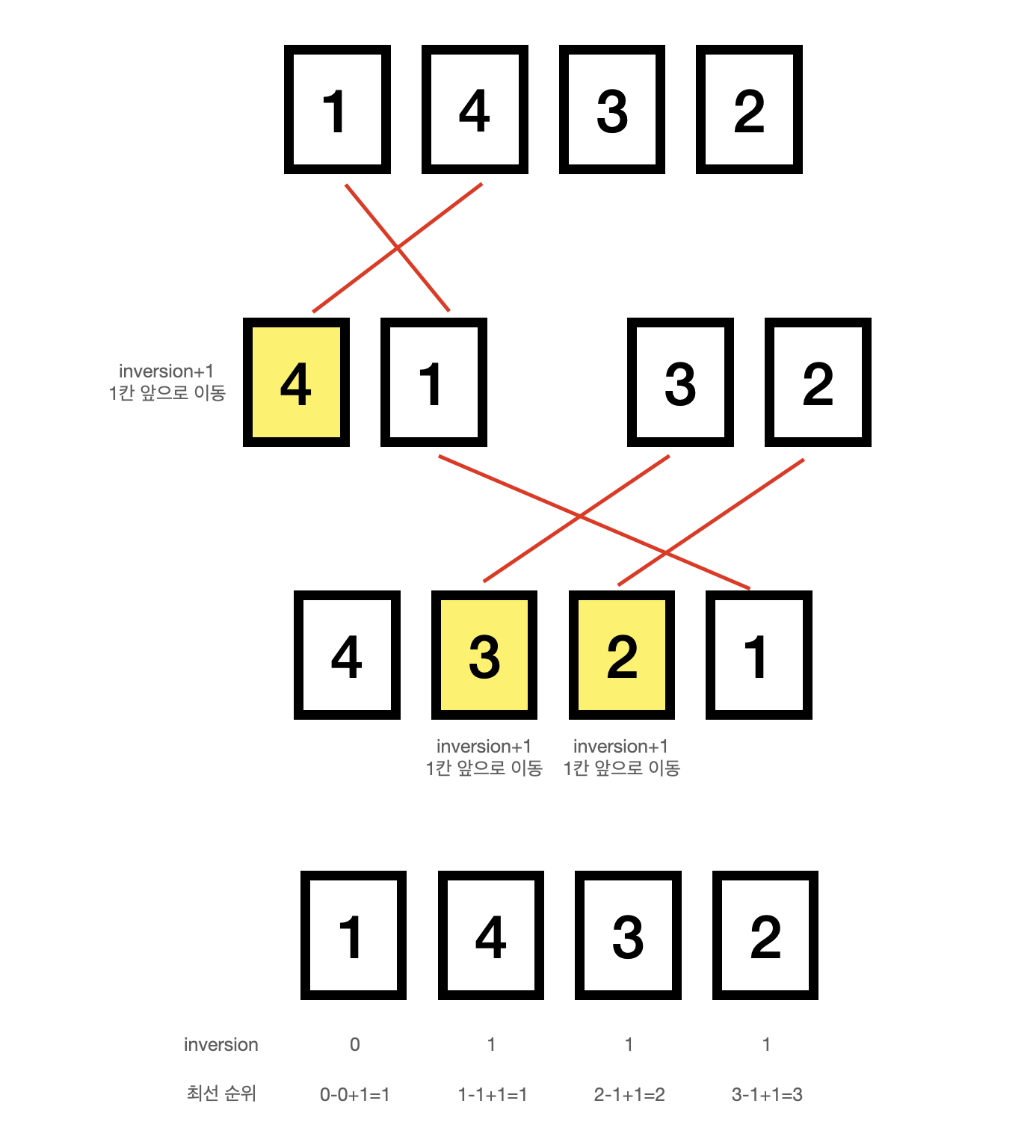
위의 그림을 보면, merging sorting 과정에서 merge 과정에서 inversion 갯수를 구할 수 있다. 뒤에 오는 값이 큰 경우 앞으로 당겨야하는데, 이는 앞에 있는 공간 만큼 당겨지기 때문에, (left_length-i)로 구할 수 있다.
이렇게, inversion을 구하게 되면, 이는 현재 인덱스를 기준으로 앞에 현재 값보다 작은 값의 갯수를 의마하게 되고, 현재 값보다 작은 경우 앞지를 수 있기 때문에 현재 인덱스에 대해 inversion갯수를 빼주게 되면 최선의 순위를 도출 할 수 있게 된다.
def mergeSort(arr):
length=len(arr)
if length<=1:
return arr
mid=length//2
left=mergeSort(arr[:mid])
right=mergeSort(arr[mid:])
return merge(left,right)
def merge(left,right):
global inversions
i,j=0,0
left_length=len(left)
right_length=len(right)
temp=[]
while i < left_length and j < right_length:
if left[i][0] > right[j][0]:
temp.append(left[i])
i+=1
else:
temp.append(right[j])
inversions[right[j][1]]+=(left_length-i)
j+=1
temp+=left[i:]
temp+=right[j:]
return temp
Full Code
def mergeSort(arr):
length=len(arr)
if length<=1:
return arr
mid=length//2
left=mergeSort(arr[:mid])
right=mergeSort(arr[mid:])
return merge(left,right)
def merge(left,right):
global inversions
i,j=0,0
left_length=len(left)
right_length=len(right)
temp=[]
while i < left_length and j < right_length:
if left[i][0] > right[j][0]:
temp.append(left[i])
i+=1
else:
temp.append(right[j])
inversions[right[j][1]]+=(left_length-i)
j+=1
temp+=left[i:]
temp+=right[j:]
return temp
def solution():
mergeSort(numbers)
for index in range(n):
print(index-inversions[index]+1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n=int(input())
numbers=[(int(input()),i) for i in range(n)]
inversions=[0]*(n+1)
solution()

댓글남기기